Sep 1, 2021
Using liquid metal to turn motion into electricity, even underwater
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: chemistry, energy, engineering
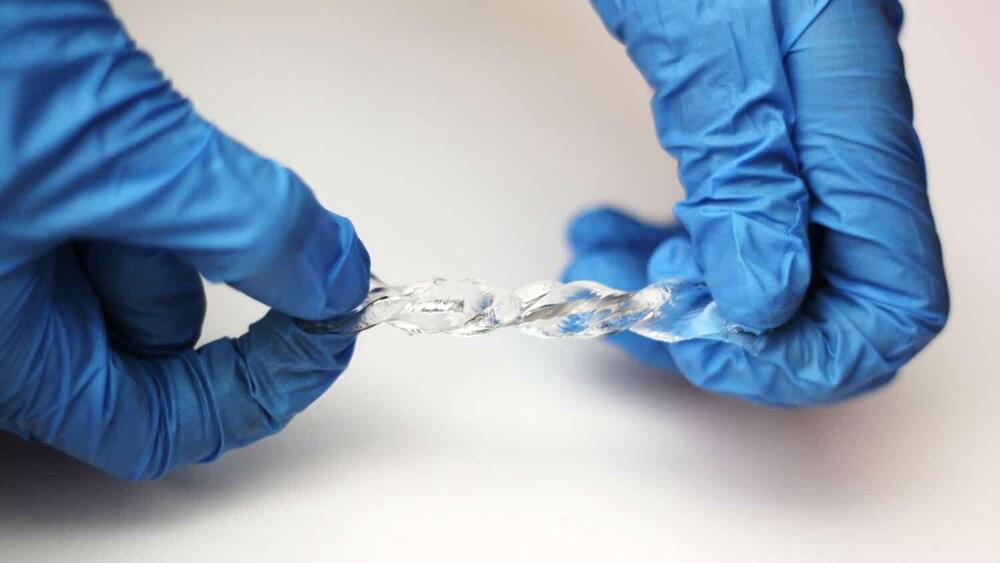
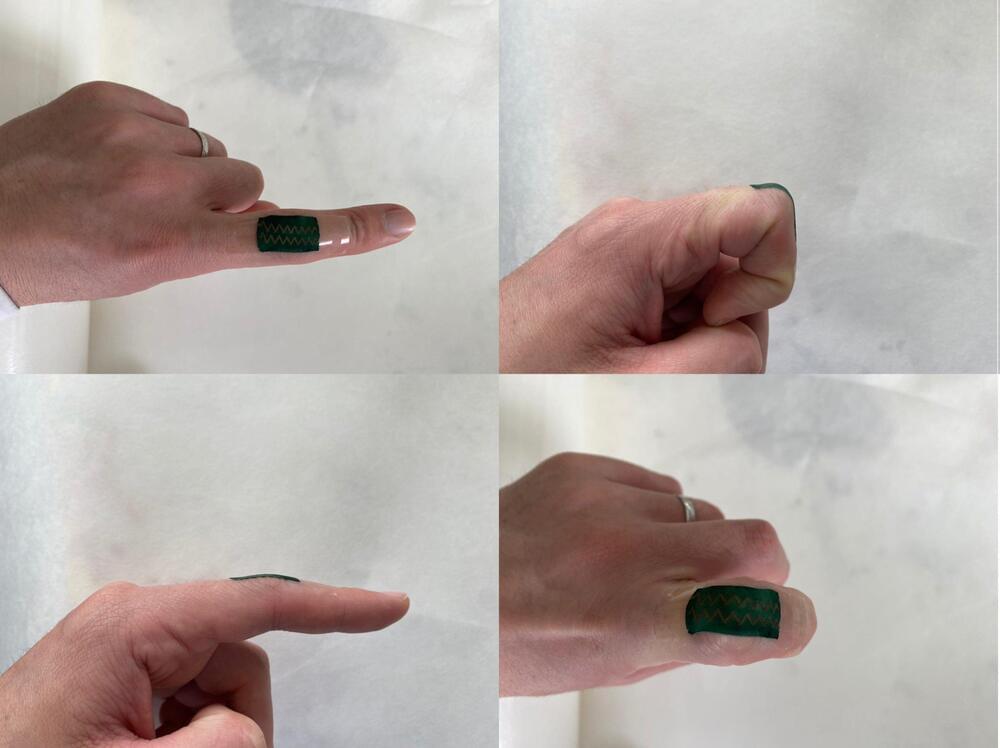
Researchers at North Carolina State University have created a soft and stretchable device that converts movement into electricity and can work in wet environments.
“Mechanical energy—such as the kinetic energy of wind, waves, body movement and vibrations from motors—is abundant,” says Michael Dickey, corresponding author of a paper on the work and Camille & Henry Dreyfus Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at NC State. “We have created a device that can turn this type of mechanical motion into electricity. And one of its remarkable attributes is that it works perfectly well underwater.”
Continue reading “Using liquid metal to turn motion into electricity, even underwater” »