Dec 10, 2024
Novel technique uses magnetic fields to probe long-term aging in batteries
Posted by Omuterema Akhahenda in categories: biotech/medical, chemistry, evolution, life extension, nuclear energy
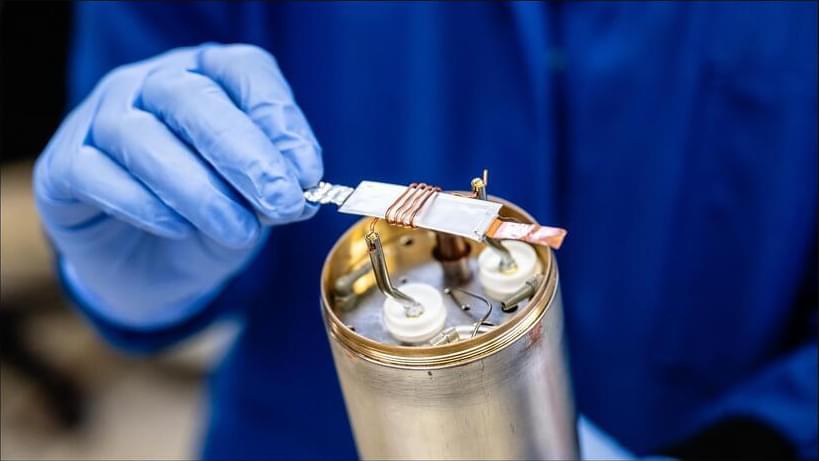
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have developed and demonstrated an innovative set of methods to evaluate long-term aging in real-world battery cells. The methods, described in a recent paper, are based on a phenomenon called nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), commonly used in medical imaging. This is the first-ever NMRspectroscopy capability that can track in fine detail how the chemistry of commercial pouch battery cells evolves over years of operation.
Argonne develops a novel method that uses nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy to characterize the chemical evolution inside battery cells over years of operation.