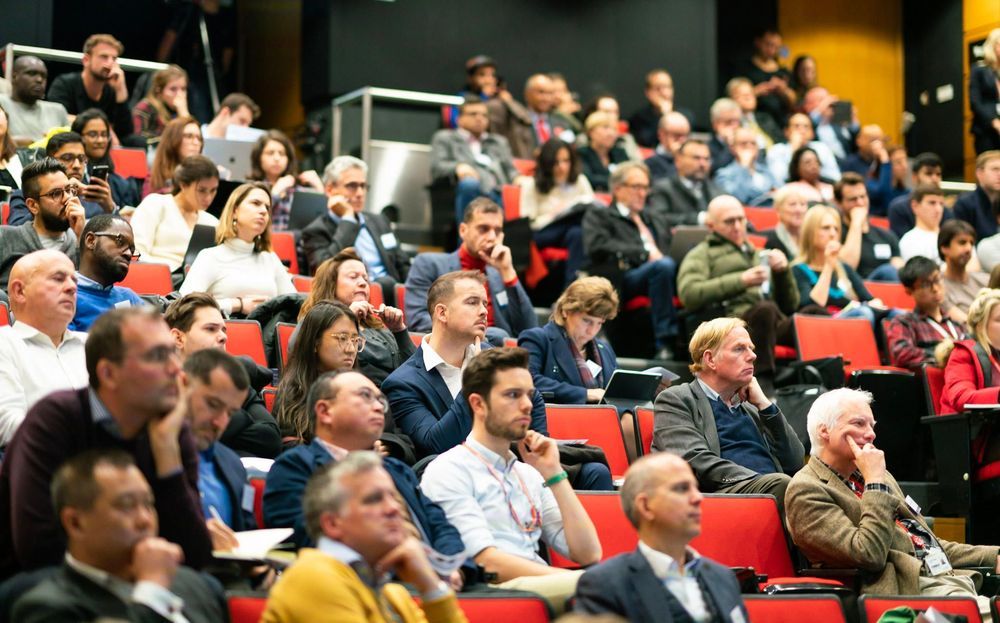
Deep Knowledge Group is delighted to have supported and participated in the landmark International Longevity Policy and Governance and AI for Longevity Summits that took place on November 12th at King’s College London, which gathered an unprecedented density and diversity of speakers and panelists at the intersection of Longevity, AI, Policy and Finance. The summits were organized by Longevity International UK and the AI Longevity Consortium at King’s College London, with the strategic support of Deep Knowledge Group, Aging Analytics Agency, Ageing Research at King’s (ARK) and the Biogerontology Research Foundation. Together they managed to attract the interest of major financial corporations, insurance companies, investment banks, Pharma and Tech corporations, and representatives of international governmental bodies, organisations and embassies, as well as leading media, and featured presentations and panel discussions from top executives and directors of Prudential, Barclays Business UK, HSBC, AXA, L&G, Longevity. Capital, Longevity Vision Fund, Juvenescence, the UK Office of AI, Microsoft, NVIDIA, Babylon Health, Huawei Europe, Insilico Medicine, Longevity International UK, the Longevity AI Consortium and others.
November 14, 2019, London, UK: Deep Knowledge Group executives Dmitry Kaminksiy and Eric Kihlstrom spoke at a landmark one-day event held yesterday at King’s College London with the strategic support Deep Knowledge Group. The event united two Longevity-themed summits under the shared strategic agenda of enabling a paradigm shift from treatment to prevention and from prevention to Precision Health via the synergistic efforts of science, industry, AI, policy and governance, to enable the UK to become an international leader in Healthy Longevity.