Oct 11, 2021
Signs of biological activities of 28,000-year-old mammoth nuclei in mouse oocytes visualized
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, genetics
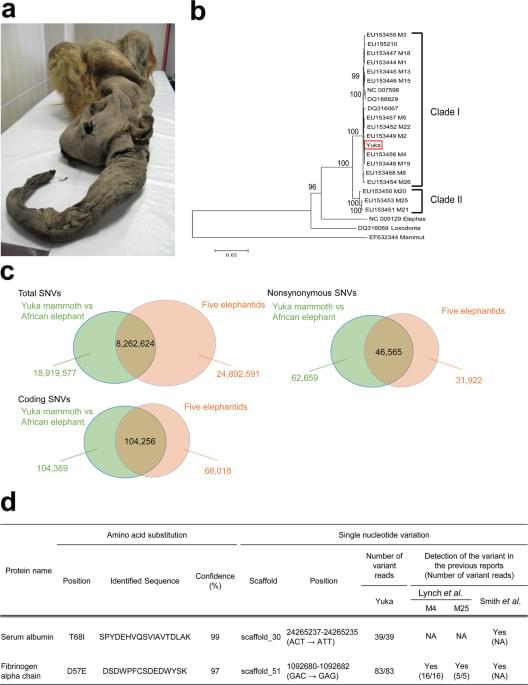
Interestingly, the nuclear protein histone H4 was detected, which is reminiscent of the retention of nuclear components in the remains (Fig. 2c). Search against the database of all mammalian species identified other nuclear proteins, such as histones, histone chaperones, proteins implicated in mRNA processing or transport and nuclear membrane proteins (Supplementary Table S2). In addition, we identified two well-characterised epigenetic modifications on histone molecules, methylation of H3K79 and H4K20 (Supplementary Fig. S2A and B), which are involved in transcriptional regulation and genome maintenance18,19. Our high-sensitive proteomic analysis suggests that the remains retain nuclear components.
These findings motivated us to seek cell nuclei from the muscle remains. Although DAPI-positive and autofluorescence-negative nucleus-like structures were rarely found (Supplementary Figs S3 and S4), we chose the autofluorescence-negative structures for the subsequent live-cell imaging of nuclear-transferred embryos since autofluorescence disturbs accurate tracing of fluorescent-tagged proteins. In total, 88 nucleus-like structures were collected from 273.5 mg mammoth tissue in 5 independent experiments (Supplementary Table S7). Our immunostaining protocol developed for single suspended cells from remains (Supplementary Fig. S5) revealed that these structures were positive for lamin B2 and histone H3, both of which were identified by mass spectrometry (Fig. 3a and Supplementary Fig. S6), suggesting that cell nuclei are, at least partially, sustained even in over a 28,000 year period.