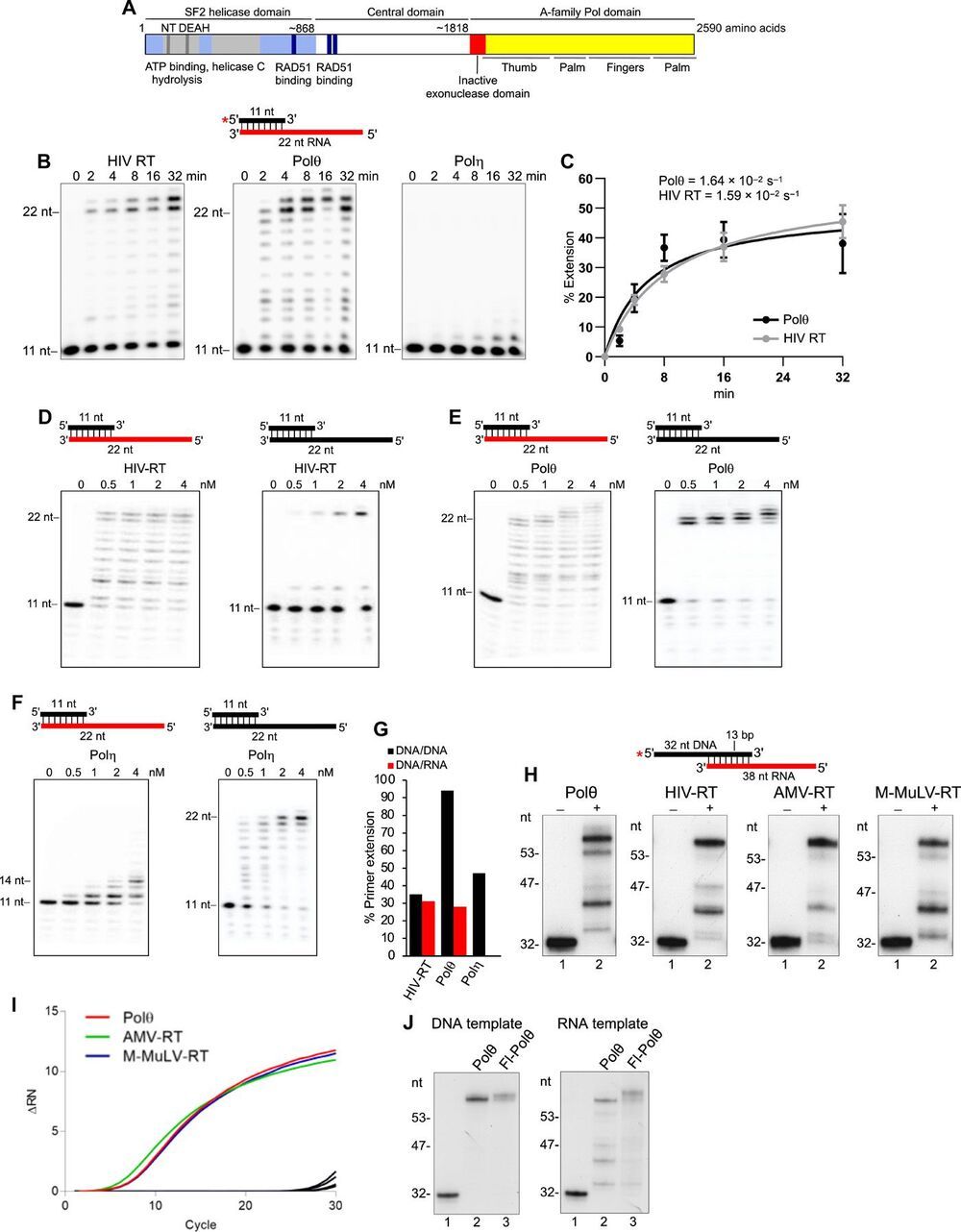
Genome-embedded ribonucleotides arrest replicative DNA polymerases (Pols) and cause DNA breaks. Whether mammalian DNA repair Pols efficiently use template ribonucleotides and promote RNA-templated DNA repair synthesis remains unknown. We find that human Polθ reverse transcribes RNA, similar to retroviral reverse transcriptases (RTs). Polθ exhibits a significantly higher velocity and fidelity of deoxyribonucleotide incorporation on RNA versus DNA. The 3.2-Å crystal structure of Polθ on a DNA/RNA primer-template with bound deoxyribonucleotide reveals that the enzyme undergoes a major structural transformation within the thumb subdomain to accommodate A-form DNA/RNA and forms multiple hydrogen bonds with template ribose 2′-hydroxyl groups like retroviral RTs. Last, we find that Polθ promotes RNA-templated DNA repair in mammalian cells. These findings suggest that Polθ was selected to accommodate template ribonucleotides during DNA repair.
Polymerase θ (Polθ) is a unique DNA polymerase-helicase fusion protein in higher eukaryotes whose A-family polymerase domain evolved from Pol I enzymes (Fig. 1A) (1, 2). However, contrary to most Pol I enzymes, Polθ is highly error-prone and promiscuous (3–6), performs translesion synthesis (TLS) opposite DNA lesions (3, 7, 8), and facilitates microhomology-mediated end-joining (MMEJ) of double-strand breaks (DSBs) by extending partially base-paired 3′ single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) overhangs at DSB repair junctions (5, 9–12). Polθ is not expressed in most tissues but is highly expressed in many cancer cells, which corresponds to a poor clinical outcome (13, 14). Furthermore, Polθ confers resistance to genotoxic cancer therapies and promotes the survival of cells deficient in DNA damage response pathways (11, 13–16). Thus, Polθ represents a promising cancer drug target.
Intriguingly, Polθ has an inactive proofreading domain due to acquired mutations (Fig. 1A) (2). Inactivating the 3′-5′ proofreading function of closely related A-family bacterial Pol I Klenow fragment (KF) enables this polymerase to reverse transcribe RNA like retroviral reverse transcriptases (RTs), which lack proofreading activity (fig. S1A) (17, 18). Because Polθ is highly error-prone and promiscuous and contains an inactive proofreading domain, we hypothesized that it has RNA-dependent DNA synthesis activity. Given that ribonucleotides are the most frequently occurring nucleotide lesion in genomic DNA that arrest replicative Pols and cause DNA breaks (19, 20), we also envisaged that Polθ would tolerate template ribonucleotides during its DNA repair activities and thus promote RNA-templated DNA repair synthesis (RNA-DNA repair). Although RNA-DNA repair mechanisms have been demonstrated in genetically engineered yeast cells (21, 22), they remain obscure in mammalian cells.