Scientific knowledge can progress rapidly, yet its social, economic, and political impacts often unfold at a painstakingly slow pace. The medicine of the 21st century draws upon genetic and embryological breakthroughs of the 19th century. Our current technology is firmly grounded in quantum physics, which was formulated a century ago. And the topic of the day, artificial intelligence (AI), traces its origins to the secret weapons research during World War II.
In 1935, the brilliant British mathematician, Alan Turing, envisioned a conceptual computer. His genius would later lead him to crack the Enigma code used by German submarines for secret communications during the war. Turing’s contributions extended beyond cryptography, as he introduced fundamental concepts of AI, including the training of artificial neural networks. Benedict Cumberbatch portrayed Turing in the 2014 film The Imitation Game, which earned a screenplay Oscar that year. All this historical context brings us to the heart of the current AI revolution.
AI uses neural networks, also known as artificial neural networks, which are comprised of multiple layers of artificial neurons. Each neuron receives numerous inputs from the lower layer and produces a single output to the upper layer, similar to the dendrites and axon of natural neurons. As information progresses through each layer, it gradually becomes more abstract, resembling the process that occurs in the visual cortex of our brains.




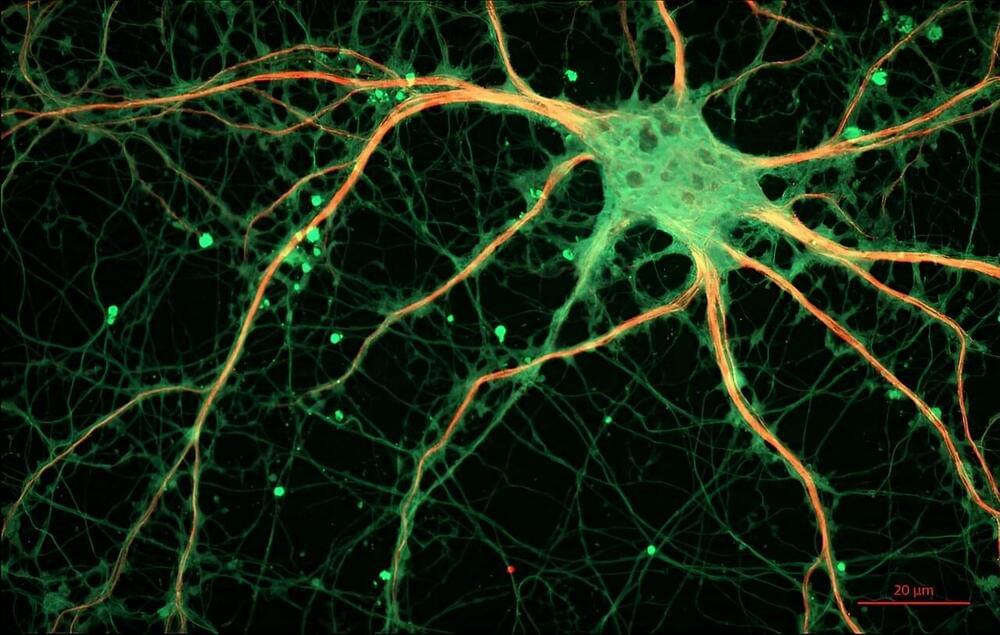

 Animals exhibit a diverse behavioral repertoire when exploring new environments and can learn which actions or action sequences produce positive outcomes. Dopamine release upon encountering reward is critical for reinforcing reward-producing actions
Animals exhibit a diverse behavioral repertoire when exploring new environments and can learn which actions or action sequences produce positive outcomes. Dopamine release upon encountering reward is critical for reinforcing reward-producing actions