Feb 16, 2023
Antidepressants can induce mutation and enhance persistence toward multiple antibiotics
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: biotech/medical, health, mathematics
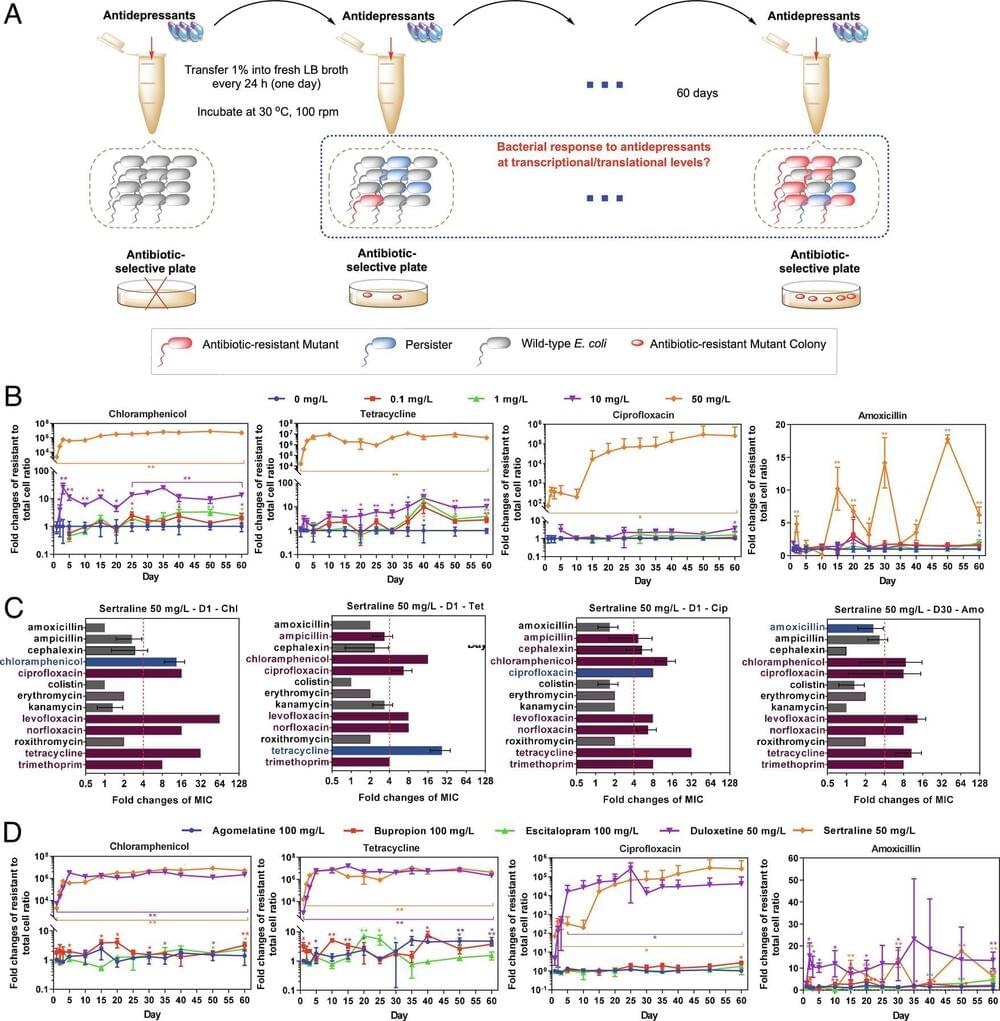
Antibiotic resistance is a global threat to public health and associated with the overuse of antibiotics. Although non-antibiotic drugs occupy 95% of the drug market, their impact on the emergence and spread of antibiotic resistance remains unclear. Here we demonstrate that antidepressants, one of the most frequently prescribed drugs, can induce antibiotic resistance and persistence. Such effects are associated with increased reactive oxygen species, enhanced stress signature responses, and stimulation of efflux pump expression. Mathematical modeling also supported a role for antidepressants in the occurrence of antibiotic-resistant mutants and persister cells. Considering the high consumption of antidepressants (16,850 kg annually in the United States alone), our findings highlight the need to re-evaluate the antibiotic-like side effects of antidepressants.