Oct 26, 2024
Researchers flip genes on and off with AI-designed DNA switches
Posted by Arthur Brown in categories: biotech/medical, genetics, health, robotics/AI
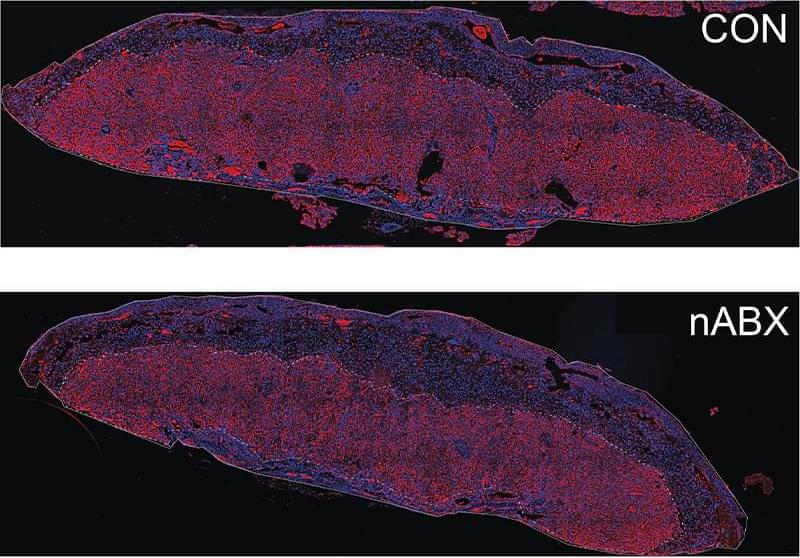
Researchers at The Jackson Laboratory (JAX), the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, and Yale University, have used artificial intelligence to design thousands of new DNA switches that can precisely control the expression of a gene in different cell types. Their new approach opens the possibility of controlling when and where genes are expressed in the body, for the benefit of human health and medical research, in ways never before possible.
“What is special about these synthetically designed elements is that they show remarkable specificity to the target cell type they were designed for,” said Ryan Tewhey, PhD, an associate professor at The Jackson Laboratory and co-senior author of the work. “This creates the opportunity for us to turn the expression of a gene up or down in just one tissue without affecting the rest of the body.”
In recent years, genetic editing technologies and other gene therapy approaches have given scientists the ability to alter the genes inside living cells. However, affecting genes only in selected cell types or tissues, rather than across an entire organism, has been difficult. That is in part because of the ongoing challenge of understanding the DNA switches, called cis-regulatory elements (CREs), that control the expression and repression of genes.