Oct 20, 2024
Circadian Disruption, Gut Microbiome Changes linked to Colorectal Cancer Progression
Posted by Natalie Chan in categories: biotech/medical, food, health
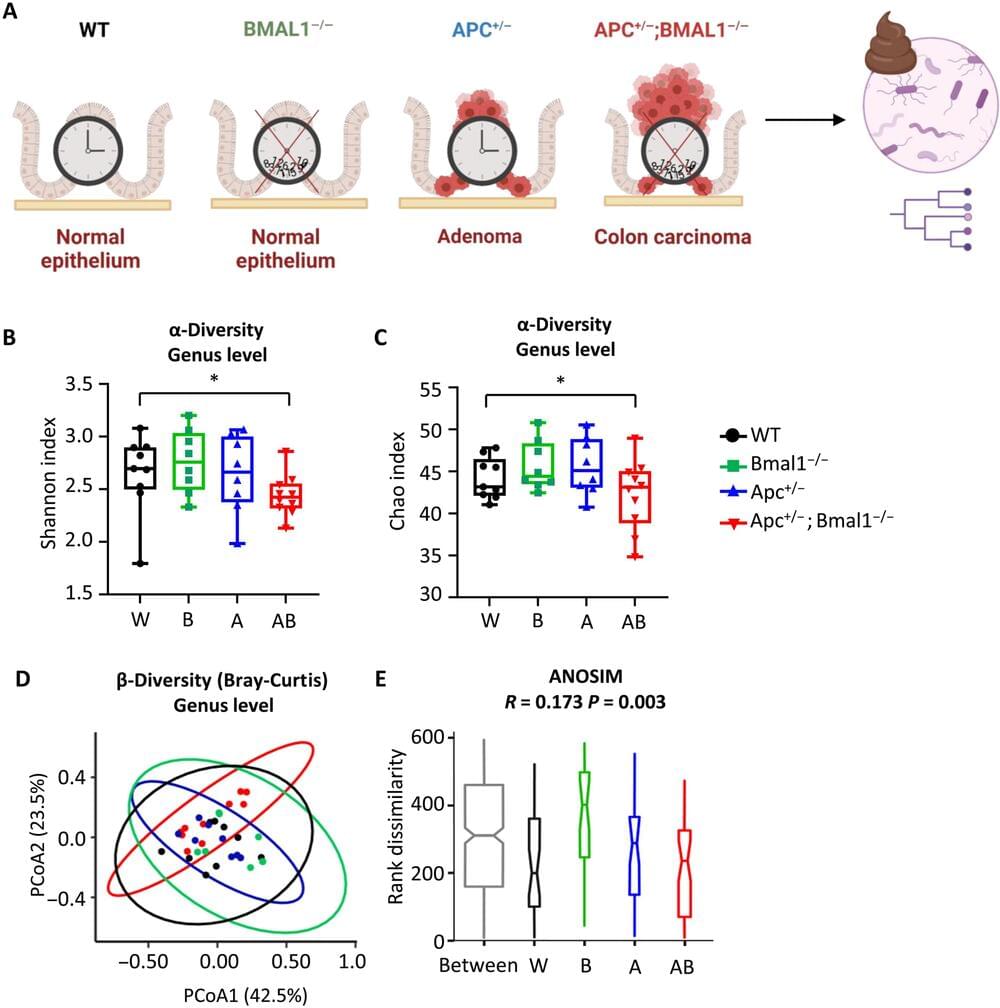
Research from the University of California, Irvine has revealed how disruption of the circadian clock, the body’s internal, 24-hour biological pacemaker, may accelerate the progression of colorectal cancer by affecting the gut microbiome and intestinal barrier function. This discovery offers new avenues for prevention and treatment strategies.
The study, published online today in the journal Science Advances, offers a more comprehensive understanding of how important changes occur in the function and composition of the gut microbiome when the circadian clock is disturbed in the presence of colorectal cancer.
“There is an alarming rise in early-onset colorectal cancer in adults under the age of 50,” said corresponding author Selma Masri, associate professor of biological chemistry. “Circadian misalignment through extended light exposure, late-night meals and other environmental factors could [be] driving these cases. Our study suggests that clock disruption, particularly through lifestyle choices, may play a significant role in gut health and, subsequently, cancer risk.”