Oct 22, 2020
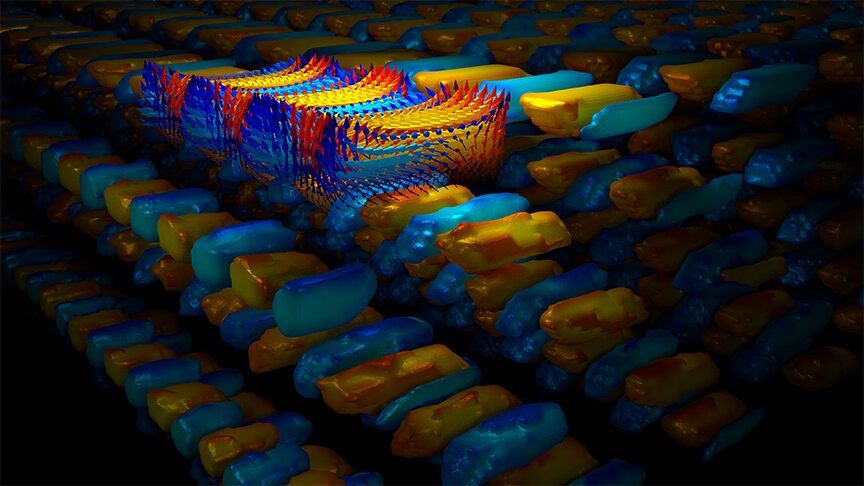
Supercrystal: A hidden phase of matter created by a burst of light
Posted by Quinn Sena in category: materials
Circa 2019
“Frustration” plus a pulse of laser light resulted in a stable “supercrystal” created by a team of researchers led by Penn State and Argonne National Laboratory, together with University of California, Berkeley, and two other national laboratories.
This is one of the first examples of a new state of matter with long-term stability transfigured by the energy from a sub-pico-second laser pulse. The team’s goal, supported by the Department of Energy, is to discover interesting states of matter with unusual properties that do not exist in equilibrium in nature.
Continue reading “Supercrystal: A hidden phase of matter created by a burst of light” »