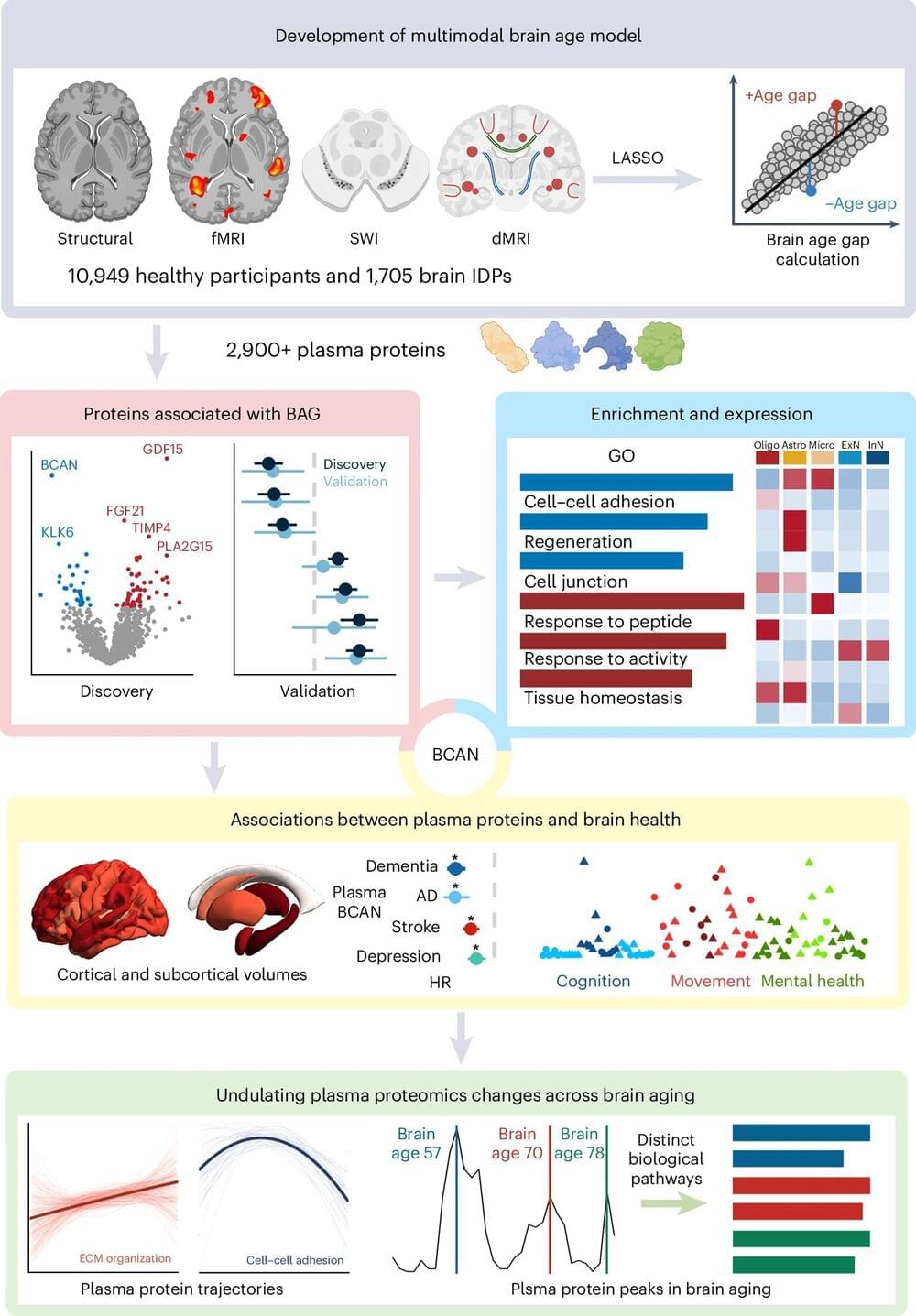
Thirteen proteins linked to brain aging in humans are identified in a Nature Aging paper. Changes in the concentrations of these blood proteins may peak at 57, 70, and 78 years old in humans, and suggest that these ages may be important for potential interventions in the brain aging process.
It is estimated that by 2050 the number of individuals aged 65 years and over will exceed 1.5 billion globally, highlighting the need for a deeper understanding of the aging process—particularly in relation to the brain.
The prevalence of neurodegenerative disorders, such as dementia, is known to increase with aging; however, effective therapies are still limited. The early identification of and intervention in brain aging could help us to prevent such disorders.