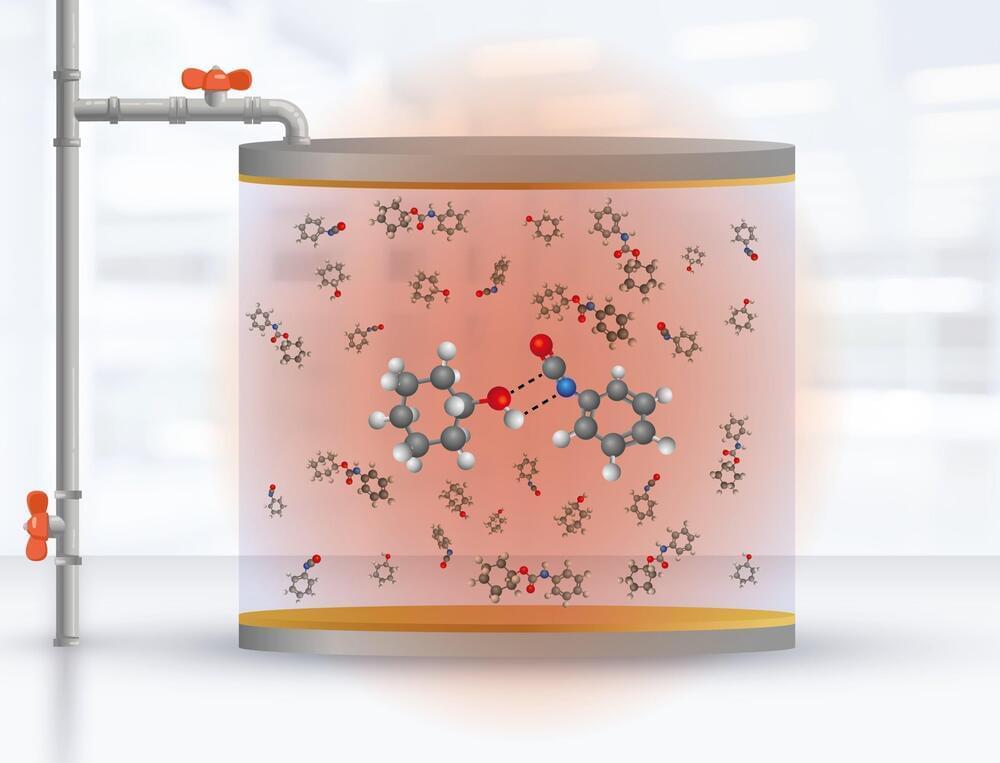
Controlling chemical reactions to generate new products is one of the biggest challenges in chemistry. Developments in this area impact industry, for example, by reducing the waste generated in the manufacture of construction materials or by improving the production of catalysts to accelerate chemical reactions.
For this reason, in the field of polariton chemistry—which uses tools of chemistry and quantum optics—in the last 10 years different laboratories around the world have developed experiments in optical cavities to manipulate the chemical reactivity of molecules at room temperature, using electromagnetic fields. Some have succeeded in modifying chemical reactions products in organic compounds, but to date, and without relevant advances in the last two years, no research team has been able to come up with a general physical mechanism to describe the phenomenon and to reproduce it to obtain the same measurements in a consistent manner.
Now a team of researchers from Universidad de Santiago (Chile), part of the Millennium Institute for Research in Optics (MIRO), led by principal investigator Felipe Herrera, and the laboratory of the chemistry division of the US Naval Research Laboratory, (United States), led by researcher Blake Simpkins, for the first time report the manipulation of the formation rate of urethane molecules in a solution contained inside an infrared cavity.