Sep 30, 2024
‘Squeezing’ increases accuracy out of quantum measurements
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in category: quantum physics
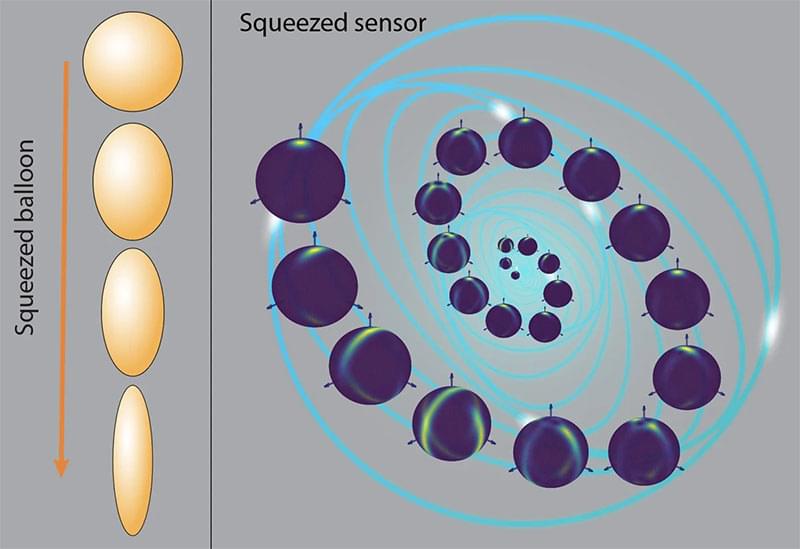
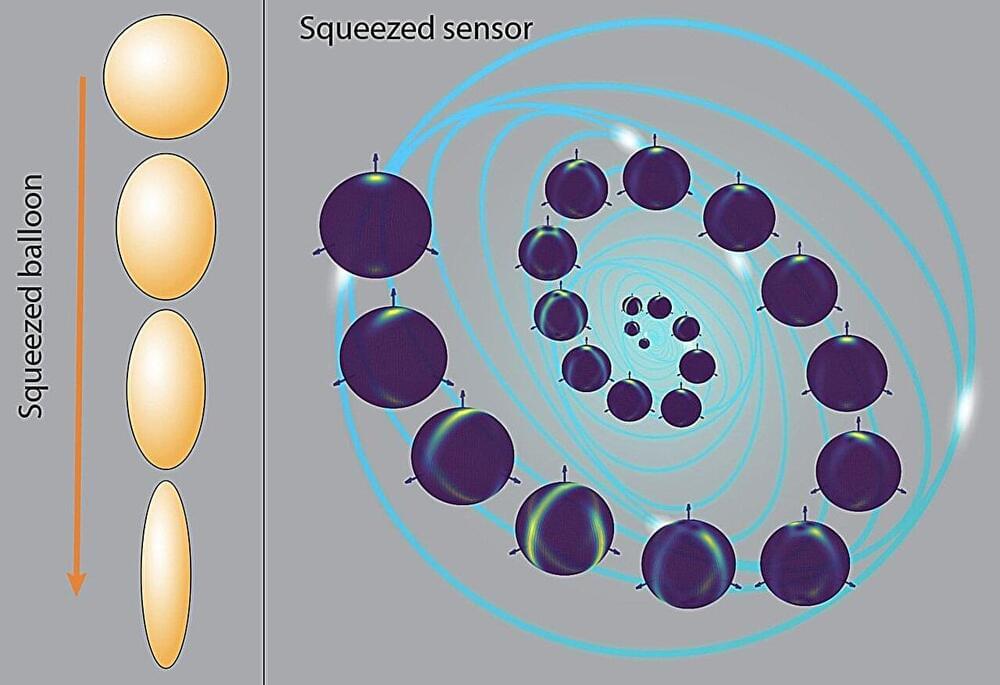
Quantum squeezing is a concept in quantum physics where the uncertainty in one aspect of a system is reduced while the uncertainty in another related aspect is increased. Imagine squeezing a round balloon filled with air. In its normal state, the balloon is perfectly spherical. When you squeeze one side, it gets flattened and stretched out in the other direction. This represents what is happening in a squeezed quantum state: you are reducing the uncertainty (or noise) in one quantity, like position, but in doing so, you increase the uncertainty in another quantity, like momentum. However, the total uncertainty remains the same, since you are just redistributing it between the two. Even though the overall uncertainty remains the same, this ‘squeezing’ allows you to measure one of those variables with much greater precision than before.
This technique has already been used to improve the accuracy of measurements in situations where only one variable needs to be precisely measured, such as in improving the precision of atomic clocks. However, using squeezing in cases where multiple factors need to be measured simultaneously, such as an object’s position and momentum, is much more challenging.
In a research paper published in Physical Review Research (“Squeezing-induced quantum-enhanced multiphase estimation”), Tohoku University’s Dr. Le Bin Ho explores the effectiveness of the squeezing technique in enhancing the precision of measurements in quantum systems with multiple factors. The analysis provides theoretical and numerical insights, aiding in the identification of mechanisms for achieving maximum precision in these intricate measurements.