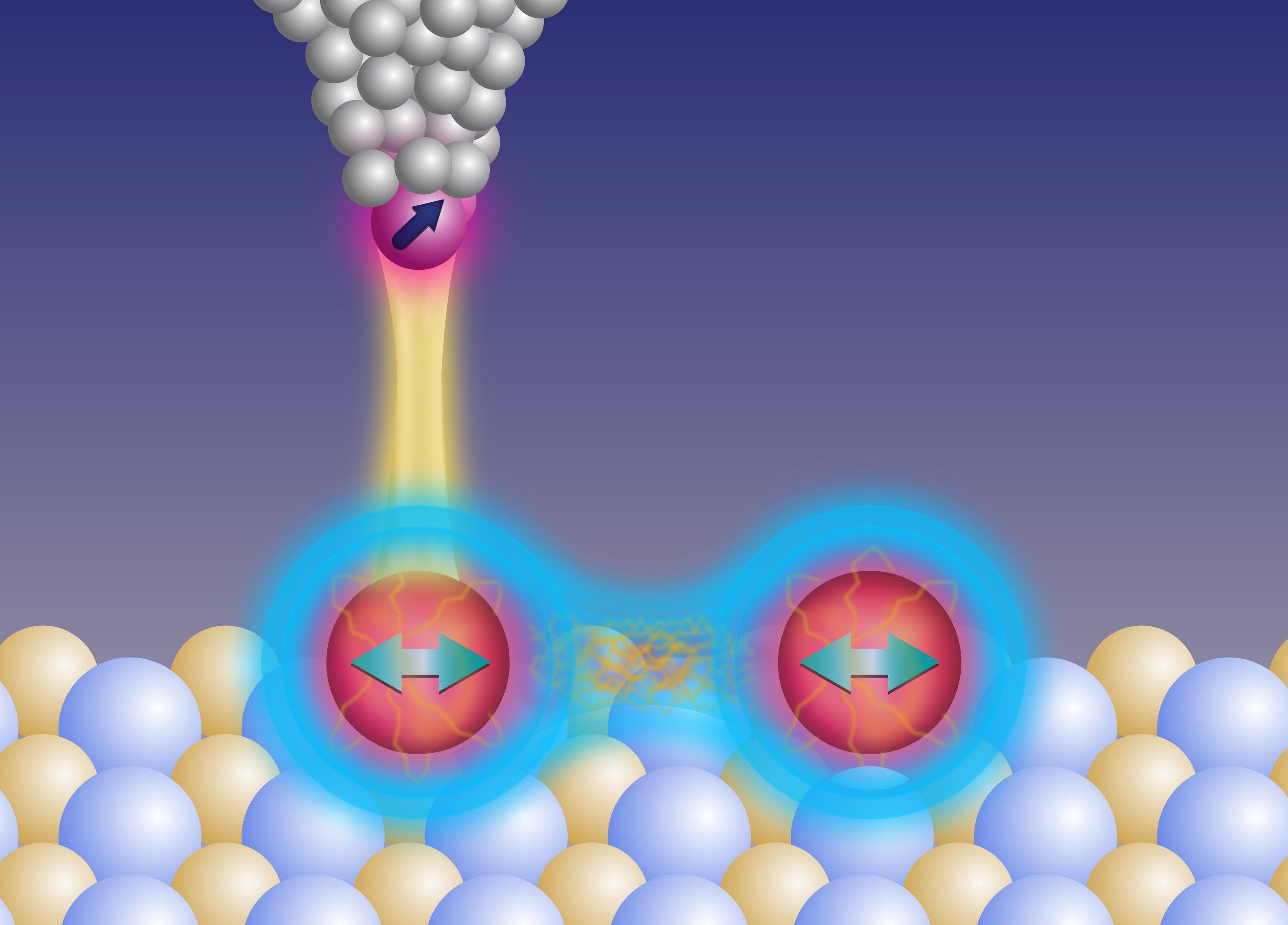
Researchers at the Center for Quantum Nanoscience (QNS) within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) achieved a major breakthrough in shielding the quantum properties of single atoms on a surface. The scientists used the magnetism of single atoms, known as spin, as a basic building block for quantum information processing. The researchers could show that by packing two atoms closely together they could protect their fragile quantum properties much better than for just one atom.
The spin is a fundamental quantum mechanical object and governs magnetic properties of materials. In a classical picture, the spin often can be considered like the needle of a compass. The north or south poles of the needle, for example, can represent spin up or down. However, according to the laws of quantum mechanics, the spin can also point in both directions at the same time. This superposition state is very fragile since the interaction of the spin with the local environment causes dephasing of the superposition. Understanding the dephasing mechanism and enhancing the quantum coherence are one of the key ingredients toward spin-based quantum information processing.
In this study, published in the journal Science Advances in November 9, 2018, QNS scientists tried to suppress the decoherence of single atoms by assembling them closely together. The spins, for which they used single titanium atoms, were studied by using a sharp metal tip of a scanning tunneling microscope and the atoms’ spin states were detected using electron spin resonance. The researchers found that by bringing the atoms very close together (1 million times closer than a millimeter), they could protect the superposition states of these two magnetically coupled atoms 20 times longer compared to an individual atom.
Read more