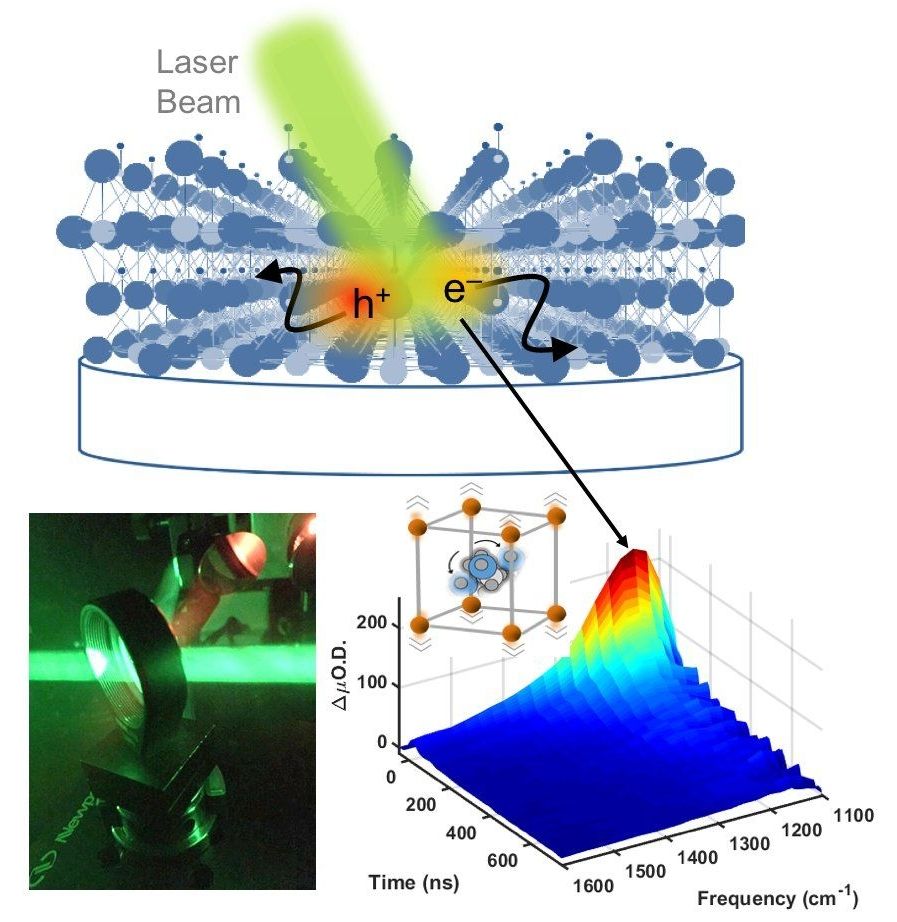
Oct 4, 2018
Artificial enzymes convert solar energy into hydrogen gas
Posted by Bill Kemp in categories: bioengineering, biological, chemistry, genetics, solar power, sustainability
In a new scientific article, researchers at Uppsala University describe how, using a completely new method, they have synthesised an artificial enzyme that functions in the metabolism of living cells. These enzymes can utilize the cell’s own energy, and thereby enable hydrogen gas to be produced from solar energy.
Hydrogen gas has long been noted as a promising energy carrier, but its production is still dependent on fossil raw materials. Renewable hydrogen gas can be extracted from water, but as yet the systems for doing so have limitations.
In the new article, published in the journal Energy and Environmental Science, an interdisciplinary European research group led by Uppsala University scientists describe how artificial enzymes convert solar energy into hydrogen gas. This entirely new method has been developed at the University in the past few years. The technique is based on photosynthetic microorganisms with genetically inserted enzymes that are combined with synthetic compounds produced in the laboratory. Synthetic biology has been combined with synthetic chemistry to design and create custom artificial enzymes inside living organisms.
Continue reading “Artificial enzymes convert solar energy into hydrogen gas” »