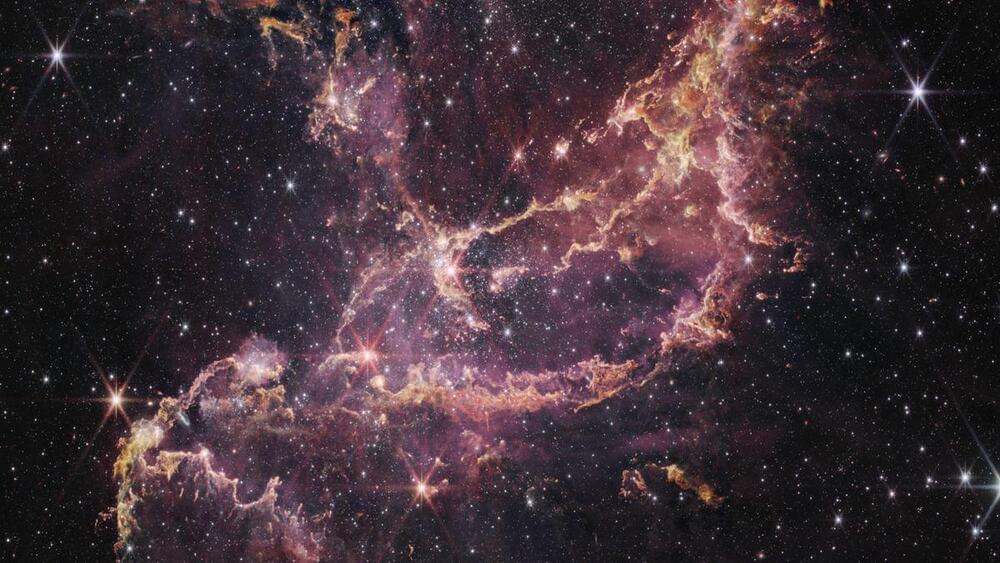
Dwarf galaxies like the SMC are often un-evolved when it comes to their chemistry because their history of star formation isn’t very extensive, so they haven’t had a chance to build up many heavy elements, such as carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, silicon or iron. NGC 346, for instance, contains about 10% the abundance of heavy elements that star-forming regions in our Milky Way galaxy have. This makes clusters such as NGC 346 great proxies for studying conditions akin to those found in the early universe.
NGC 346 is still forming lots of stars, and JWST found that many of the young ones, with ages of 20 to 30 million years, still possess planet-forming disks around them. Their existence confounds expectations.
“With Webb, we have a strong confirmation of what we saw with Hubble, and we must rethink how we create computer models for planet formation and early evolution in the young universe,” said Guido De Marchi of the European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC) in the Netherlands, who led the research.