Circa 2020 Simulation of the human brain.
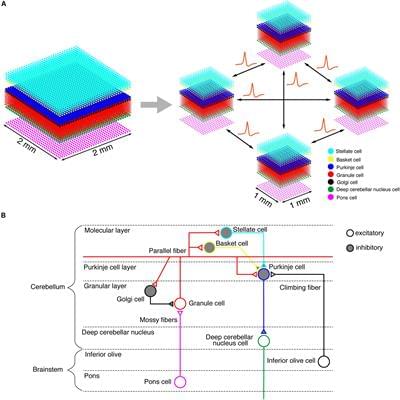
Computer simulation of the human brain at an individual neuron resolution is an ultimate goal of computational neuroscience. The Japanese flagship supercomputer, K, provides unprecedented computational capability toward this goal. The cerebellum contains 80% of the neurons in the whole brain. Therefore, computer simulation of the human-scale cerebellum will be a challenge for modern supercomputers. In this study, we built a human-scale spiking network model of the cerebellum, composed of 68 billion spiking neurons, on the K computer. As a benchmark, we performed a computer simulation of a cerebellum-dependent eye movement task known as the optokinetic response. We succeeded in reproducing plausible neuronal activity patterns that are observed experimentally in animals. The model was built on dedicated neural network simulation software called MONET (Millefeuille-like Organization NEural neTwork), which calculates layered sheet types of neural networks with parallelization by tile partitioning. To examine the scalability of the MONET simulator, we repeatedly performed simulations while changing the number of compute nodes from 1,024 to 82,944 and measured the computational time. We observed a good weak-scaling property for our cerebellar network model. Using all 82,944 nodes, we succeeded in simulating a human-scale cerebellum for the first time, although the simulation was 578 times slower than the wall clock time. These results suggest that the K computer is already capable of creating a simulation of a human-scale cerebellar model with the aid of the MONET simulator.
Computer simulation of the whole human brain is an ambitious challenge in the field of computational neuroscience and high-performance computing (Izhikevich, 2005; Izhikevich and Edelman, 2008; Amunts et al., 2016). The human brain contains approximately 100 billion neurons. While the cerebral cortex occupies 82% of the brain mass, it contains only 19% (16 billion) of all neurons. The cerebellum, which occupies only 10% of the brain mass, contains 80% (69 billion) of all neurons (Herculano-Houzel, 2009). Thus, we could say that 80% of human-scale whole brain simulation will be accomplished when a human-scale cerebellum is built and simulated on a computer. The human cerebellum plays crucial roles not only in motor control and learning (Ito, 1984, 2000) but also in cognitive tasks (Ito, 2012; Buckner, 2013). In particular, the human cerebellum seems to be involved in human-specific tasks, such as bipedal locomotion, natural language processing, and use of tools (Lieberman, 2014).