Dec 11, 2020
Stretchable sensor gives robots and VR a human touch
Posted by John Gallagher in categories: augmented reality, robotics/AI, virtual reality
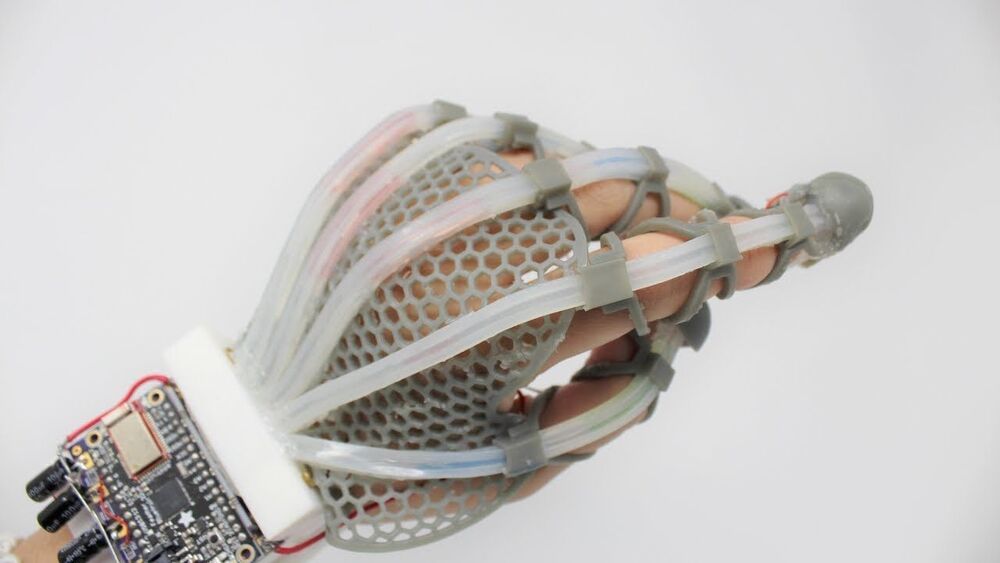
It’s not a stretch to say that stretchable sensors could change the way soft robots function and feel. In fact, they will be able to feel quite a lot.
Cornell researchers have created a fiber-optic sensor that combines low-cost LEDs and dyes, resulting in a stretchable “skin” that detects deformations such as pressure, bending and strain. This sensor could give soft robotic systems – and anyone using augmented reality technology – the ability to feel the same rich, tactile sensations that mammals depend on to navigate the natural world.