Butterflies can see more of the world than humans, including more colors and the field oscillation direction, or polarization, of light. This special ability enables them to navigate with precision, forage for food and communicate with one another. Other species, like the mantis shrimp, can sense an even wider spectrum of light, as well as the circular polarization, or spinning states, of light waves. They use this capability to signal a “love code,” which helps them find and be discovered by mates.
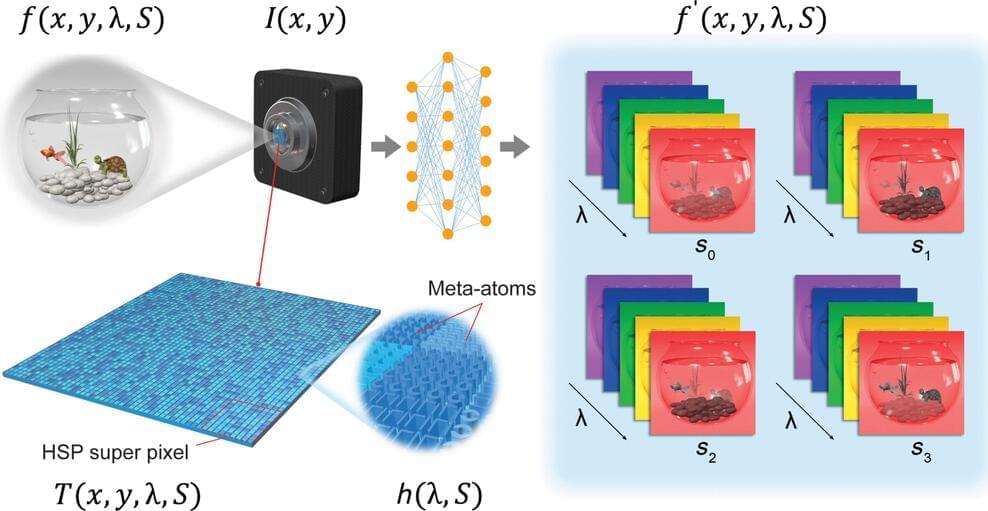
Inspired by these abilities in the animal kingdom, a team of researchers at the Penn State College of Engineering has developed an ultrathin optical element known as a metasurface, which can attach to a conventional camera and encode the spectral and polarization data of images captured in a snapshot or video through tiny, antenna-like nanostructures that tailor light properties. A machine learning framework, also developed by the team, then decodes this multi-dimensional visual information in real-time on a standard laptop.
The researchers have published their work in Science Advances.