Aug 7, 2018
Research reveals molecular details of sperm-egg fusion
Posted by Genevieve Klien in category: futurism
The fusion of a sperm cell with an egg cell is the very first step in the process that leads to new individuals in sexually reproducing species. Fundamental as this process may be, scientists are only now beginning to understand the complexities of how it works.
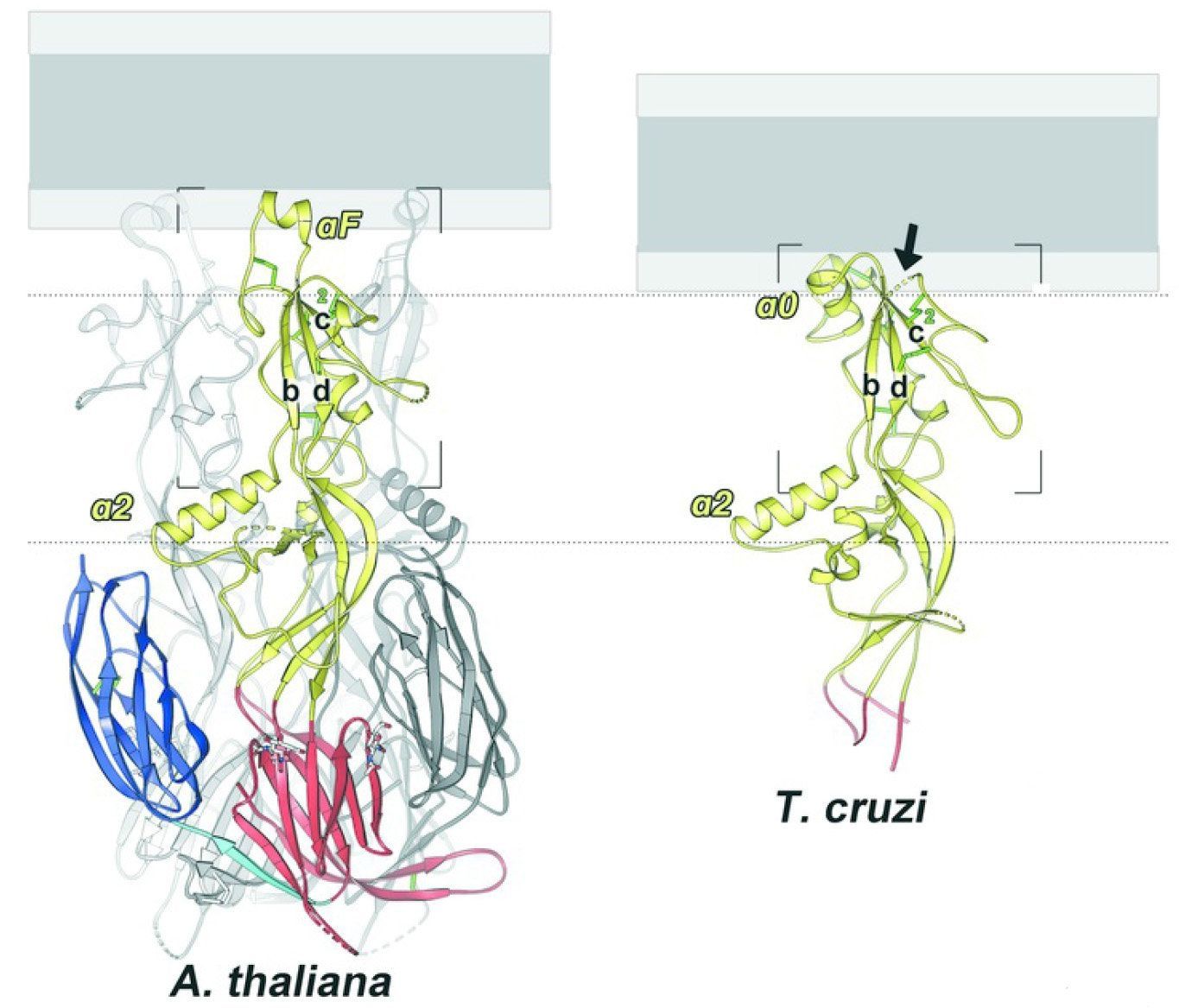
In a paper published in PLOS Biology, researchers have described the detailed structure of proteins that enable sperm-egg fusion in two different species: a flowering plant and a protozoan. The researchers hope that revealing the process in these species and their relatives might bring scientists a step closer to understanding it across sexual species, including humans and other vertebrates.
“It’s surprising to me that we still don’t know how a human sperm fuses with a human egg,” said Mark Johnson, an associate professor of biology at Brown University and a study co-author. “One of the things we hope this paper will do is establish a structural signature for the proteins that make gamete fusion work in these species so that we might be able to look for it in species where those protein mechanisms are still unknown.”