Nov 20, 2024
First pairs of white dwarf–main sequence binaries discovered in clusters shine new light on stellar evolution
Posted by Saúl Morales Rodriguéz in categories: chemistry, cosmology, physics
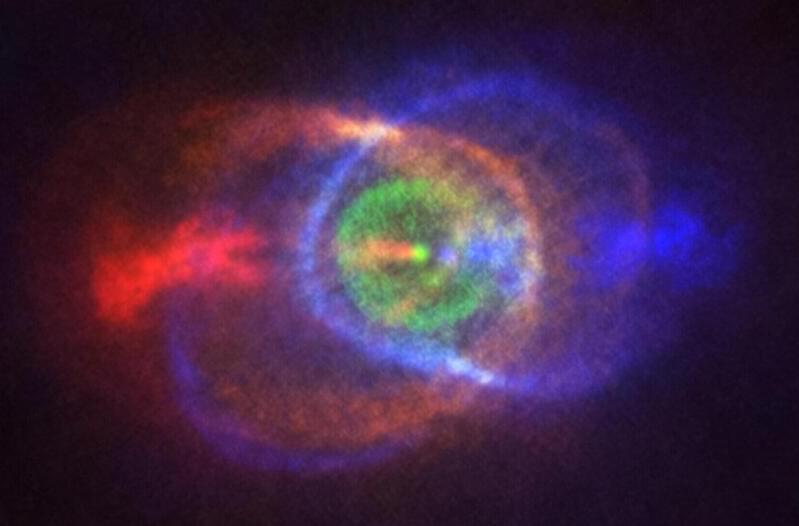
Astronomers at the University of Toronto (U of T) have discovered the first pairs of white dwarf and main sequence stars—” dead” remnants and “living” stars—in young star clusters. Described in a new study published in The Astrophysical Journal, this breakthrough offers new insights into an extreme phase of stellar evolution, and one of the biggest mysteries in astrophysics.
Scientists can now begin to bridge the gap between the earliest and final stages of binary star systems—two stars that orbit a shared center of gravity—to further our understanding of how stars form, how galaxies evolve, and how most elements on the periodic table were created. This discovery could also help explain cosmic events like supernova explosions and gravitational waves, since binaries containing one or more of these compact dead stars are thought to be the origin of such phenomena.
Most stars exist in binary systems. In fact, nearly half of all stars similar to our sun have at least one companion star. These paired stars usually differ in size, with one star often being more massive than the other. Though one might be tempted to assume that these stars evolve at the same rate, more massive stars tend to live shorter lives and go through the stages of stellar evolution much faster than their lower mass companions.