Jan 14, 2023
Chemists cook up brand-new kind of nanomaterial
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: chemistry, nanotechnology
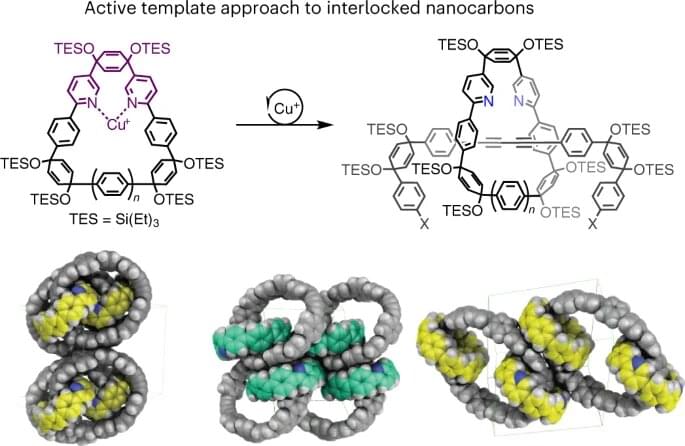
There’s a new nanomaterial on the block. University of Oregon chemists have found a way to make carbon-based molecules with a unique structural feature: interlocking rings.
Like other nanomaterials, these linked-together molecules have interesting properties that can be “tuned” by changing their size and chemical makeup. That makes them potentially useful for an array of applications, such as specialized sensors and new kinds of electronics.
“It’s a new topology for carbon nanomaterials, and we’re finding new properties that we haven’t been able to see before,” said James May, a graduate student in chemistry professor Ramesh Jasti’s lab and the first author on the paper. May and his colleagues report their findings in a paper published in Nature Chemistry.