Archive for the ‘food’ category: Page 101
Jul 23, 2022
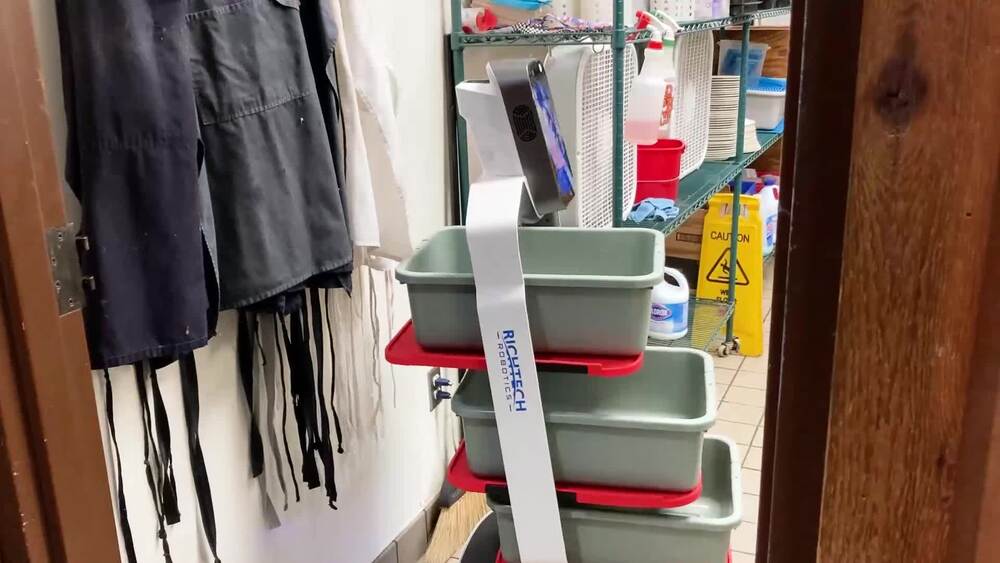
Else Labs Announces Pro Kitchen Focused Oliver Fleet As It Pauses Rollout of Home Cooking Robot
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: food, habitats, robotics/AI
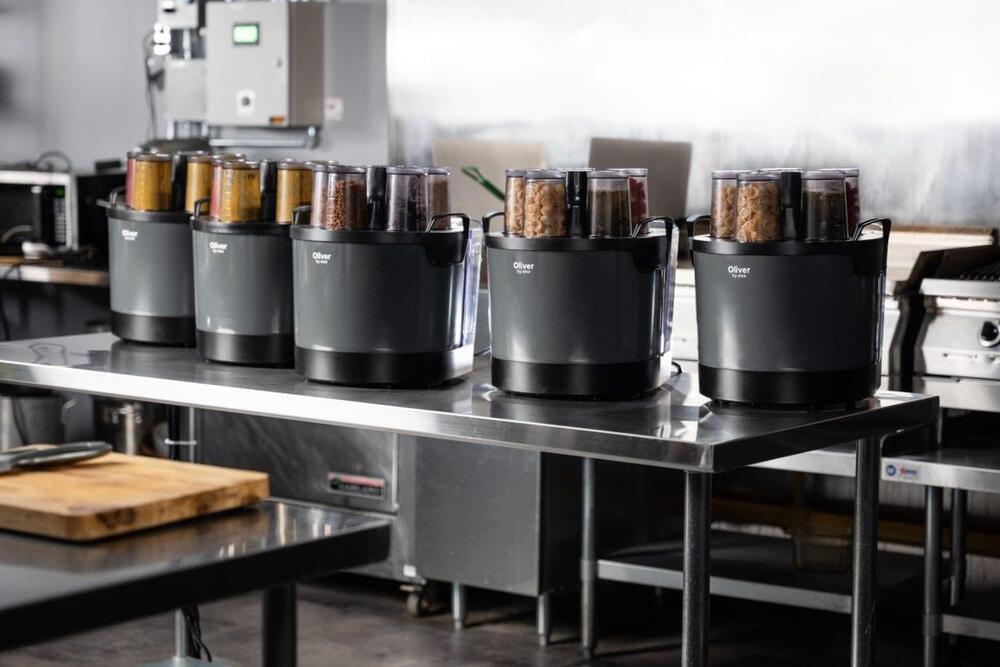

Else Labs, the company behind the countertop home cooking robot called Oliver, announced today the launch of Oliver Fleet, a commercial kitchen reimagining of its original core product.
The new Fleet solution is a respin of its original standalone Oliver home cooking robot into a solution that allows multiple units to be used and managed simultaneously in professional kitchen environments to automate cooking tasks. According to company CEO Khalid Aboujassoum, while the Oliver Fleet units look the same from the outside as the original consumer unit, they’ve been built to withstand the more rugged requirements of the professional kitchen.
Jul 23, 2022
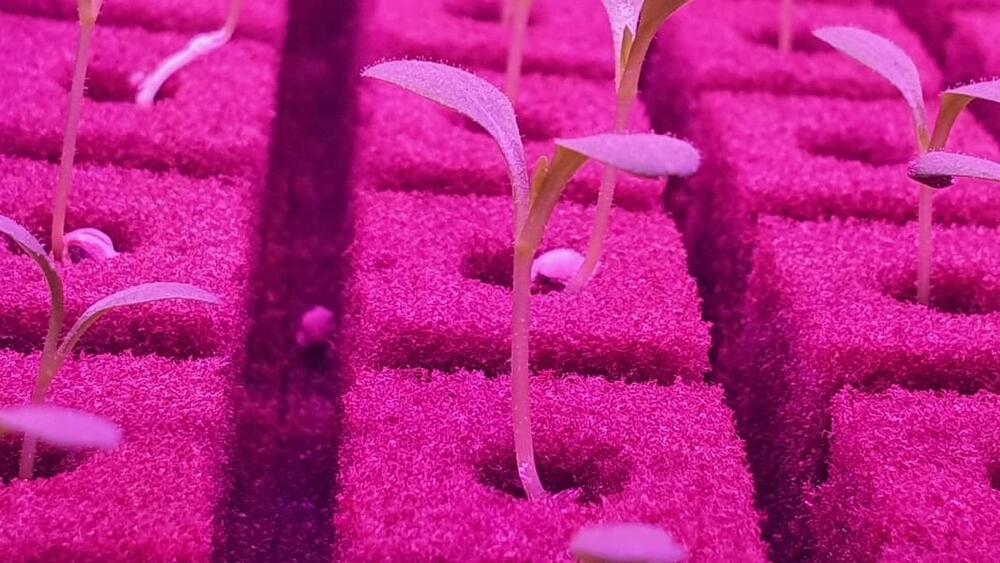
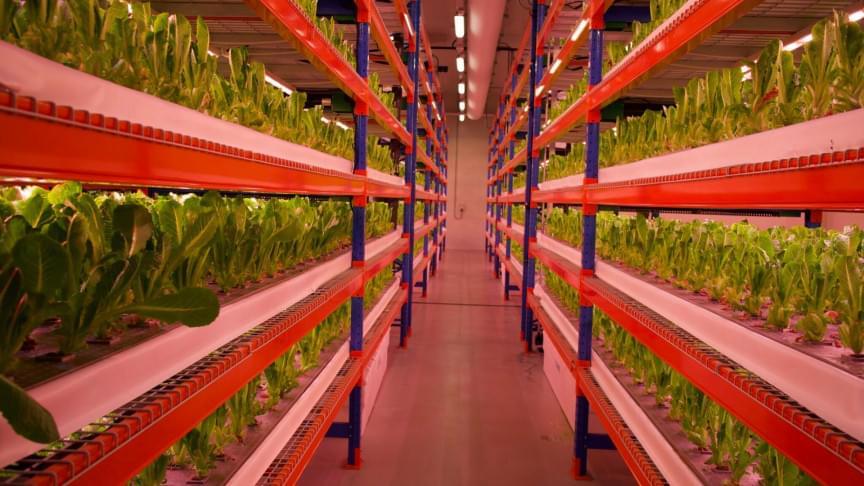
The World’s Biggest Vertical Farm Just Opened in Dubai
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: business, chemistry, food, nanotechnology, solar power, sustainability
The Dubai facility has the capacity to produce over two million pounds of leafy greens annually, and will grow lettuces, arugula, mixed salad greens, and spinach.
ECO stands for Emirates Crop One; the vertical farm is a joint venture between Crop One Holdings (a Massachusetts-based vertical farming company) and Emirates Flight Catering (the catering business that serves Emirates Airlines). Greens from the vertical farm will be served onboard Emirates flights, and will also be sold in grocery stores in the UAE. Since they’re grown in a sterile environment without pesticides, herbicides, or chemicals, the greens come ready-to-eat and don’t need to be washed.
The UAE is in many ways an ideal location for vertical farming, if not a place where the technology may soon become essential. It gets an abundance of sunlight but doesn’t have much water to speak of (it was, fittingly, the field testing site for a nanoparticle technology that helps sandy soil retain water and nutrients); that means vertical farms could use energy from solar panels to grow food indoors using 95 percent less water than traditional agriculture.
Jul 22, 2022
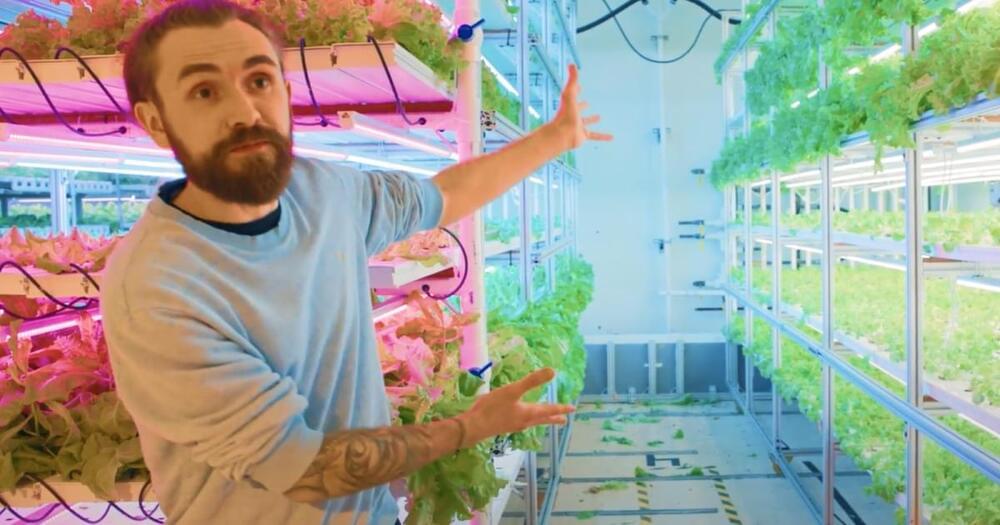
Why growing food indoors is the future of farming 
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: food, futurism
Jul 22, 2022
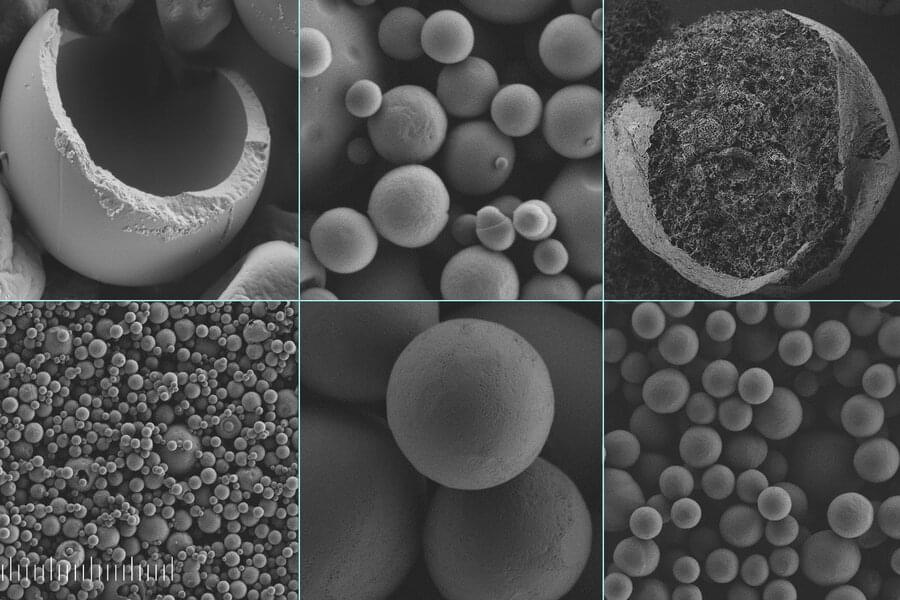
MIT researchers develop silk capsules to replace microplastics
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: food, sustainability
Researchers have created a biodegradable system based on silk to replace the microplastics used in paints, cosmetics, and agricultural products.
Jul 22, 2022
Silk offers alternative to some microplastics
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: chemistry, engineering, food
Microplastics, tiny particles of plastic that are now found worldwide in the air, water, and soil, are increasingly recognized as a serious pollution threat, and have been found in the bloodstream of animals and people around the world.
Some of these microplastics are intentionally added to a variety of products, including agricultural chemicals, paints, cosmetics, and detergents—amounting to an estimated 50,000 tons a year in the European Union alone, according to the European Chemicals Agency. The EU has already declared that these added, nonbiodegradable microplastics must be eliminated by 2025, so the search is on for suitable replacements, which do not currently exist.
Now, a team of scientists at MIT and elsewhere has developed a system based on silk that could provide an inexpensive and easily manufactured substitute. The new process is described in a paper in the journal Small, written by MIT postdoc Muchun Liu, MIT professor of civil and environmental engineering Benedetto Marelli, and five others at the chemical company BASF in Germany and the U.S.
Jul 22, 2022
Bananas and salmon help counter effect of salt in women’s diet, study finds
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: biotech/medical, food
Eating foods such as bananas, avocados and salmon could help reduce the negative effects of salt in women’s diet, research suggests.
The study found that potassium-rich diets were associated with lower blood pressure, particularly in women with high salt intake.
Jul 19, 2022
The world’s largest vertical farm using 95% less water opens in Dubai
Posted by Gemechu Taye in categories: food, sustainability
Jul 19, 2022
The food crisis in Nigeria is extremely concerning — World Food Programme (WFP)
Posted by Quinn Sena in category: food
The United Nations (U.N.) has released a report indicating that food insecurity in parts of Nigeria has reached “catastrophic” levels.
Jul 19, 2022
The missing links: Finding function in lincRNAs
Posted by Shubham Ghosh Roy in categories: biotech/medical, food
Genomes contain regions between protein-coding genes that produce lengthy RNA molecules that never give rise to a protein. These long intergenic non-coding RNAs (lincRNAs) are thought to have important functions, such as regulating responses to environmental change. However, a paucity of well-annotated lincRNA data, especially for crop plants, has precluded a deeper understanding of their roles.
Up until now, there have been no systematic genome-wide studies that both confirmed DNA sequences that produce lincRNAs and proposed functions for those lincRNAs. Plus, data are reported differently across studies, making direct comparisons among them difficult.
These barriers inspired researchers at the Boyce Thompson Institute to take a comprehensive look at the identity, production and function of lincRNAs in four species in the mustard family, including the model organism Arabidopsis thaliana, and Brassica rapa, a species that produces boy choy, turnips and other food crops.