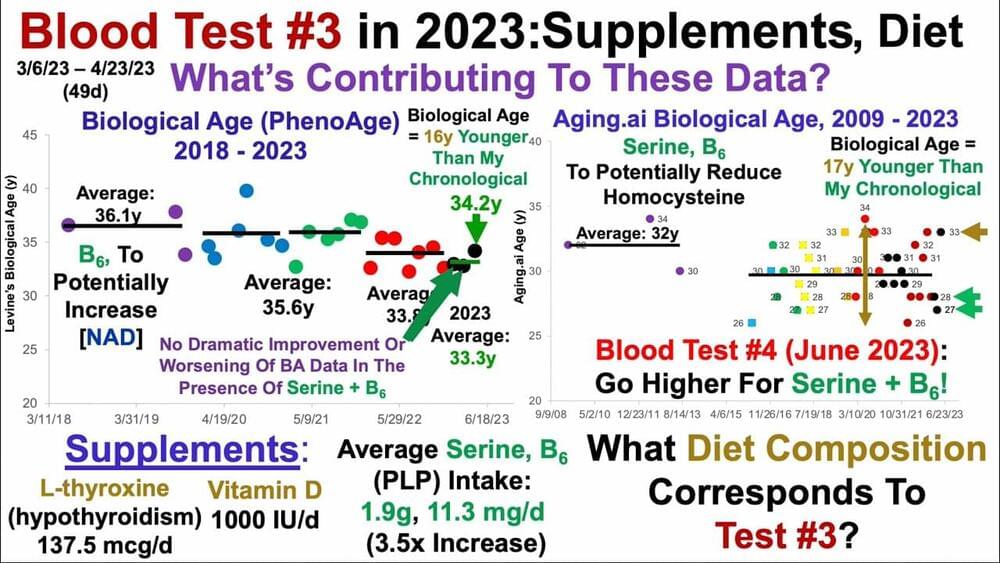
The biology underpinning a rare genetic mutation that allows its carrier to live virtually pain-free, heal more rapidly and experience reduced anxiety and fear, has been uncovered by new research from UCL.
The study, published in Brain, follows up the team’s discovery in 2019 of the FAAH-OUT gene and the rare mutations that cause Jo Cameron to feel virtually no pain and never feel anxious or afraid. The new research describes how the mutation in FAAH-OUT “turns down” FAAH gene expression, as well as the knock-on effects on other molecular pathways linked to wound healing and mood. It is hoped the findings will lead to new drug targets and open up new avenues of research in these areas.
Jo, who lives in Scotland, was first referred to pain geneticists at UCL in 2013, after her doctor noticed that she experienced no pain after major surgeries on her hip and hand. After six years of searching, they identified a new gene that they named FAAH-OUT, which contained a rare genetic mutation. In combination with another, more common mutation in FAAH, it was found to be the cause of Jo’s unique characteristics.