Archive for the ‘genetics’ category: Page 333
Feb 8, 2020
Researchers Finally Sequence Giant Squid’s Entire Genome
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, genetics
For the first time, scientists have sequenced the entire genetic code of a giant squid.
Because the massive creature has never been captured alive, biologists have largely been left in the dark as to how the giant squid grows and behaves. After sequencing its genes, University of Copenhagen and Marine Biological Laboratory researchers found several oddities in the giant squid’s DNA — genes that are rarely found in other invertebrates, for instance — giving scientists new tools with which understand the bizarre animals.
Feb 8, 2020
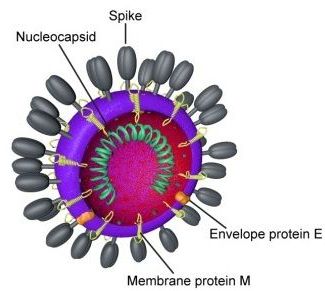
UCSC Genome Browser posts the coronavirus genome
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, genetics, government, health
Santa Cruz, CA February 7, 2020 —Research into the novel Wuhan seafood market pneumonia virus, the deadly “coronavirus” that has forced the Chinese government to quarantine more than 50 million people in the country’s dense industrial heartland, will be facilitated by the UC Santa Cruz Genomics Institute. The Genomics Institute’s Genome Browser team has posted the complete biomolecular code of the virus for researchers all over the world to use.
“When we display coronavirus data in the UCSC Genome Browser, it lets researchers look at the virus’ structure and more importantly work with it so they can research how they want to attack it,” said UCSC Genome Browser Engineer Hiram Clawson.
Samples of the virus have been processed in labs all over the world, and the raw information about its genetic code has been sent to the worldwide repository of genomic information at the National Institutes of Health’s National Center for Bioinformatics (NCBI) in Bethesda, Maryland.
Feb 8, 2020
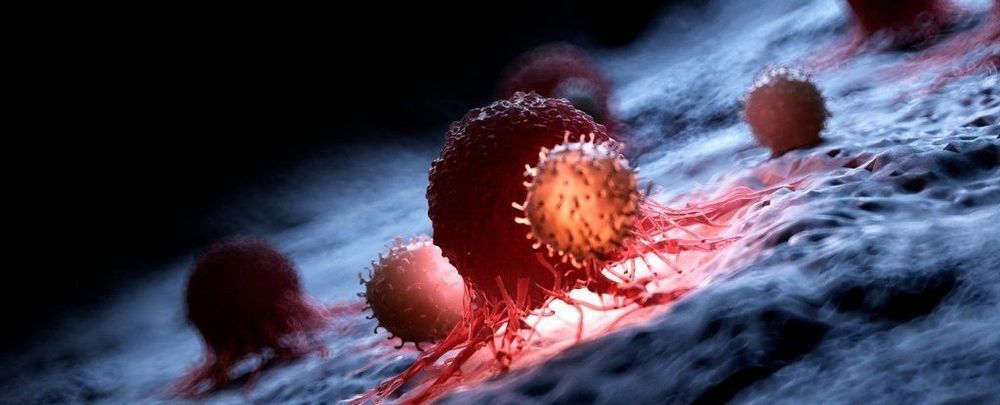
Human clinical trial suggests CRISPR feasible for fighting cancer
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, genetics

The results are in from a human clinical trial using the CRISPR/Cas9 gene-editing system to treat cancer. The study involved editing the immune cells of three cancer patients to better fight tumors, and the results show that the treated cells persist in the body for long periods and didn’t trigger any dangerous side effects.
CRISPR allows scientists to make precise edits to the genes in living cells, removing harmful genes and introducing new beneficial ones. Animal tests of the technique have shown great promise in treating a range of diseases, such as cervical cancer, muscular dystrophy and HIV.
Continue reading “Human clinical trial suggests CRISPR feasible for fighting cancer” »
Feb 8, 2020
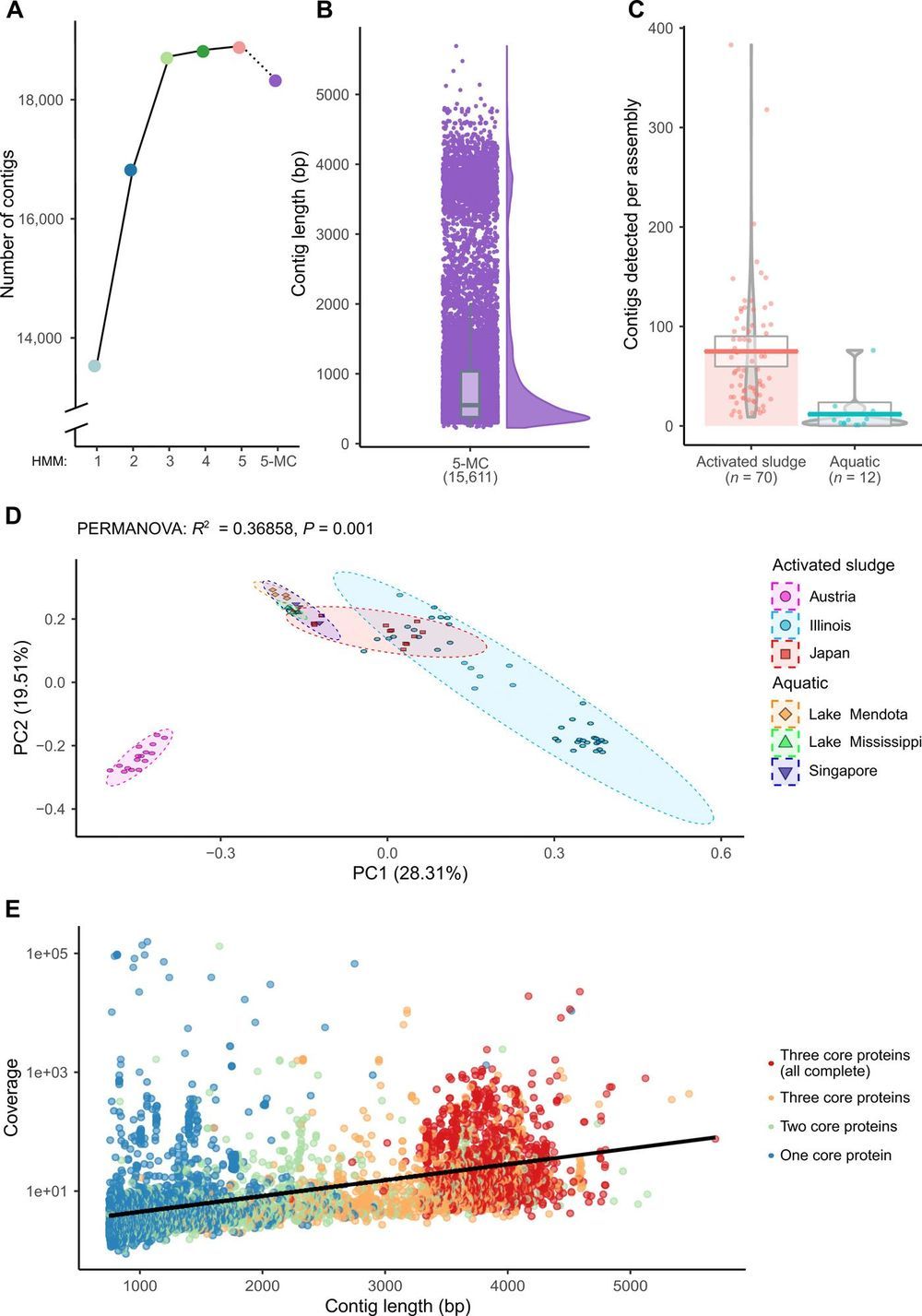
Expansion of known ssRNA phage genomes: From tens to over a thousand
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, evolution, genetics
O.o!
The first sequenced genome was that of the 3569-nucleotide single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) bacteriophage MS2. Despite the recent accumulation of vast amounts of DNA and RNA sequence data, only 12 representative ssRNA phage genome sequences are available from the NCBI Genome database (June 2019). The difficulty in detecting RNA phages in metagenomic datasets raises questions as to their abundance, taxonomic structure, and ecological importance. In this study, we iteratively applied profile hidden Markov models to detect conserved ssRNA phage proteins in 82 publicly available metatranscriptomic datasets generated from activated sludge and aquatic environments. We identified 15,611 nonredundant ssRNA phage sequences, including 1015 near-complete genomes. This expansion in the number of known sequences enabled us to complete a phylogenetic assessment of both sequences identified in this study and known ssRNA phage genomes. Our expansion of these viruses from two environments suggests that they have been overlooked within microbiome studies.
Viruses, particularly bacteriophages targeting prokaryotes, are the most diverse biological entities in the biosphere (1, 2). Currently, there are 11,489 genome sequences available in the NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) Viral RefSeq database (version 94). The vast majority of known phage have a double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) genome (3, 4). Recent metagenomic analysis of 145 marine virome sampling sites identified 195,728 DNA viral populations, highlighting that only a fraction of Earth’s viral diversity has been characterized (5). An additional expansion of known phage populations by Roux et al. (6) revealed that not only dsDNA phages but also single-stranded DNA Inoviridae are far more diverse than previously considered. The rapid expansion in viral discovery through metagenomics is enabling a greater understanding of their roles within environments and their evolutionary relationships, which is subsequently causing a revolution in phage taxonomy (7).
Continue reading “Expansion of known ssRNA phage genomes: From tens to over a thousand” »
Feb 8, 2020
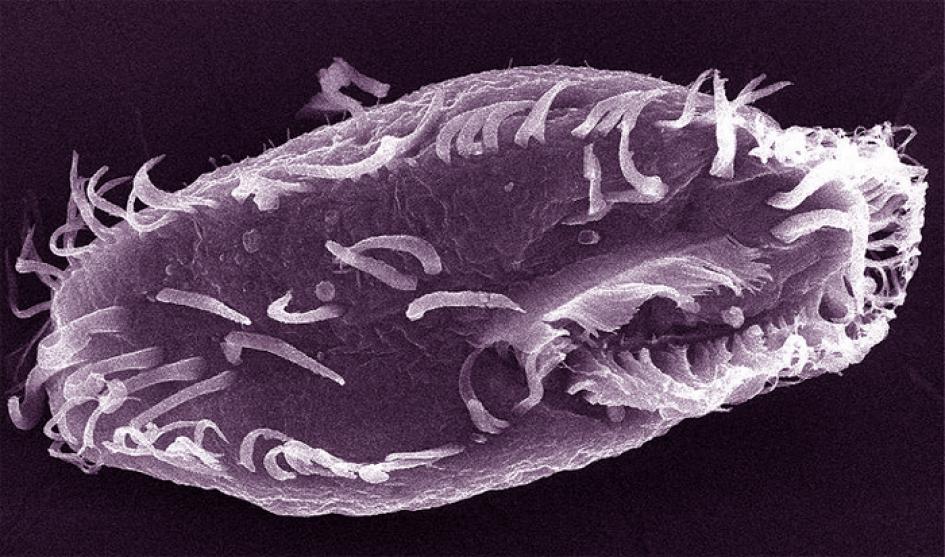
You Have 46 Chromosomes. This Pond Creature Has 15,600
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, genetics, life extension
O.o probs alien o.o circa 2013.
Remember when encyclopaedias were books, and not just websites? You’d have a shelf full of information, packaged into entries, and then into separate volumes. Your genome is organised in a similar way. Your DNA is packaged into large volumes called chromosomes. There are 23 pairs of them, each of which contains a long string of genes. And just as encyclopaedia books are bound in sturdy covers to prevent the pages within from fraying, so too are your chromosomes capped by protective structures called telomeres.
That’s basically how it works in any animal or plant or fungus. The number of chromosomes might vary a lot—fruit flies have 8 while dogs have 78—but the basic organisation is the same.
Continue reading “You Have 46 Chromosomes. This Pond Creature Has 15,600” »
Feb 8, 2020
US Trial Shows 3 Cancer Patients Had Their Genomes Altered Safely
Posted by Prem Vijaywargi in categories: biotech/medical, genetics
Researchers-genetically-alter-the-immune-system-of-cancer-patients-without-side-effect.
US scientists have succeeded in genetically editing the immune systems of three cancer patients using CRISPR, without creating any side effects, a first for the tool which is revolutionizing biomedical research.
The highly anticipated results from the first phase of a clinical trial were published in the journal Science on Thursday.
Continue reading “US Trial Shows 3 Cancer Patients Had Their Genomes Altered Safely” »
Feb 8, 2020
Sharks Have a Secret Buried in Their DNA That Could Help Humans Fight Cancer
Posted by Quinn Sena in categories: biotech/medical, food, genetics
Sharks are at the top of the marine food chain for a reason. Their massive size along with a dazzling row of extra-sharp teeth make them the fiercest hunters in our oceans. But it turns out that the shark’s aquatic dominance reaches down into its very DNA, and through its mutations, sharks could teach us how to fight our most deadly affliction—cancer.
This isn’t the first evidence that mutations can prove beneficial for disease resistance and long-term survival. High bone density, a hemoglobin that boosts malaria resistance, and a third retinal cone that improves color vision are some human examples. But new gene mapping conducted by scientists at the Save Our Seas Foundation Shark Research Center at Florida’s Nova Southeastern University, the Guy Harvey Research Institute, and the Cornell University College of Veterinary Medicine shows that sharks have developed genomic adaptations that repair damaged DNA, effectively protecting them against cancer and other diseases.
Feb 8, 2020
Ireland — World’s First “Age Friendly” Country by World Health Organization (WHO) Network — Catherine McGuigan, National Program Lead, Age Friendly Ireland — ideaXme — Ira Pastor
Posted by Ira S. Pastor in categories: aging, bioengineering, biotech/medical, economics, finance, genetics, geopolitics, governance, health, life extension

Tags: agetech, aging, bioquark, biotech, health, ideaxme, ira pastor, ireland, Life extension, longevity, regenerage, regeneration, wellness
Feb 8, 2020
Bio-Security — Dr. Tara O’Toole MD, EVP and Senior Fellow at In-Q-Tel, director of B.Next, former Under Secretary for the Science and Technology Directorate at the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) — ideaXme — Ira Pastor
Posted by Ira S. Pastor in categories: aging, biological, biotech/medical, defense, DNA, genetics, government, health, life extension, science
Tags: bioquantine, bioquark, biosecurity, cia, Cold War, coronavirus, defense, dhs, epidemiology, health, ideaxme, intelligence, ira pastor, outbreak, pandemic, virology, virome, wellness