Nov 23, 2024
New gene drive reverses insecticide resistance in pests… then disappears
Posted by Dan Breeden in categories: bioengineering, biotech/medical, chemistry, food, genetics, health
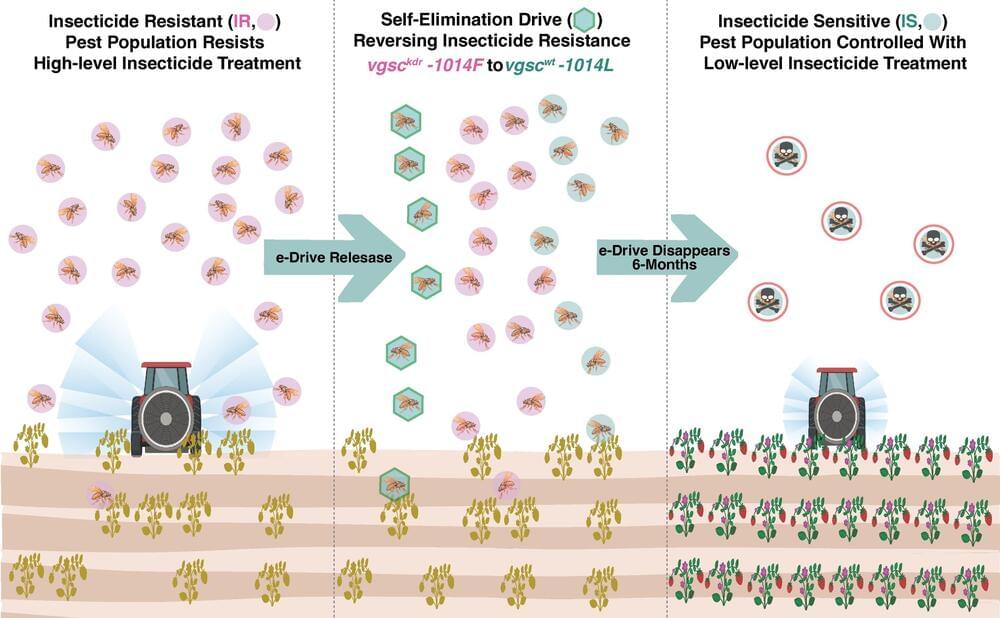
Insecticides have been used for centuries to counteract widespread pest damage to valuable food crops. Eventually, over time, beetles, moths, flies and other insects develop genetic mutations that render the insecticide chemicals ineffective.
Escalating resistance by these mutants forces farmers and vector control specialists to ramp up use of poisonous compounds at increasing frequencies and concentrations, posing risks to human health and damage to the environment since most insecticides kill both ecologically important insects as well as pests.
To help counter these problems, researchers recently developed powerful technologies that genetically remove insecticide-resistant variant genes and replace them with genes that are susceptible to pesticides. These gene-drive technologies, based on CRISPR gene editing, have the potential to protect valuable crops and vastly reduce the amount of chemical pesticides required to eliminate pests.