Dec 19, 2024
Astronaut-on-a-chip: Multi-organ tissue chips simulate space radiation’s impact on human health
Posted by Genevieve Klien in categories: biotech/medical, computing, health
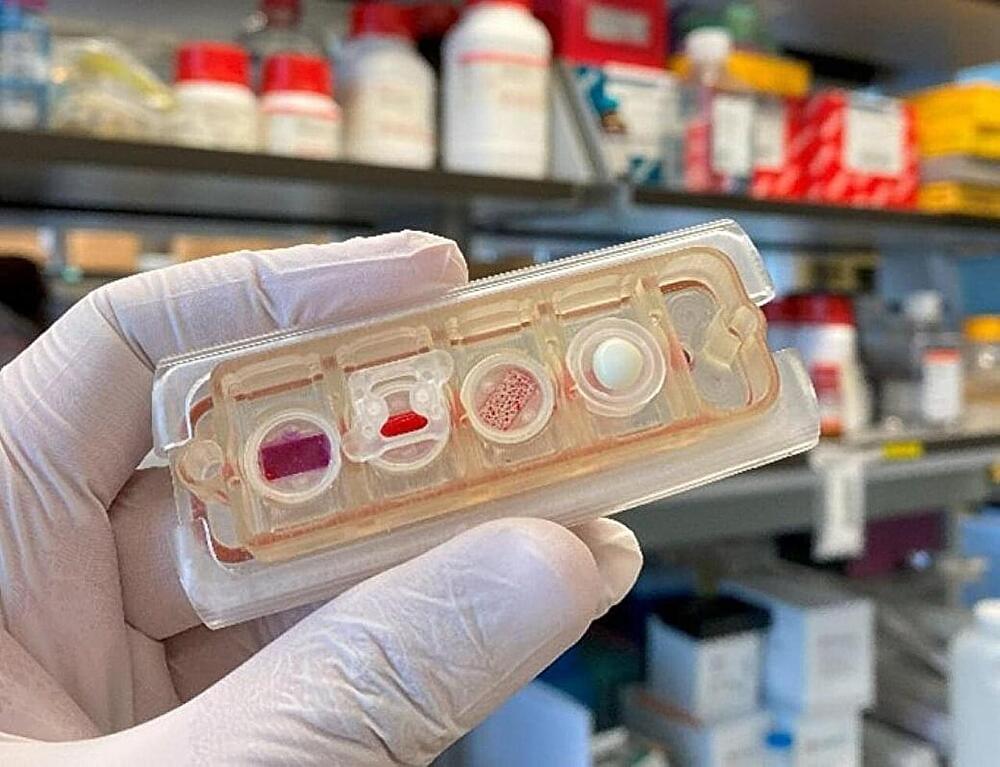
As astronauts venture further into space, their exposure to harmful radiation rises. Researchers from Columbia University are simulating the effects of space radiation here on Earth to determine its impact on human physiology using multi-organ tissue chips. Their work documents the differential effects seen in tissues after acute and prolonged radiation exposure and identifies multiple genes of interest that could help inform the development of future radioprotective agents.
Their study appears in Advanced Science.
“As deep space exploration continues to unfold, it is vital to understand the physiological damage caused by space radiation to better mitigate its effects. By exposing multi-organ models to simulated cosmic radiation, this study has laid the groundwork to aid in this effort,” commented Jermont Chen, Ph.D., a program director in the Division of Discovery Science and Technology at NIBIB.