Mar 19, 2024
Microsoft Forms New AI Division to Push Copilot to Consumers
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in category: robotics/AI
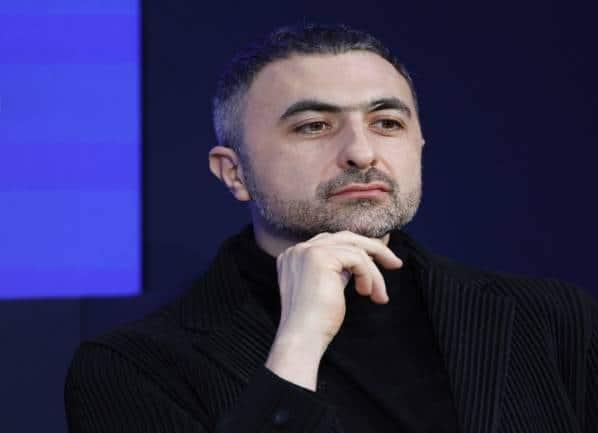
He then left Google and started a new AI lab called Inflection AI, which he ran as CEO. He and Inflection’s chief scientist, Karén Simonyan, are now jumping ship to help lead Microsoft AI.
Suleyman will become both a Microsoft EVP and run the new Microsoft AI group as CEO. On why he was selected, Nadella said: “I’ve known Mustafa for several years and have greatly admired him as a founder of both DeepMind and Inflection, and as a visionary, product maker, and builder of pioneering teams that go after bold missions.”
Meanwhile, Suleyman noted in a LinkedIn post: “I’ll be leading all consumer AI products and research, including Copilot, Bing and Edge.” Several of his co-workers at Inflection have also decided to migrate to Microsoft, he wrote.