Oct 7, 2024
Scientists are now planning to ‘grow’ ice and ‘refreeze’ Arctic Sea
Posted by Paul Battista in categories: climatology, sustainability
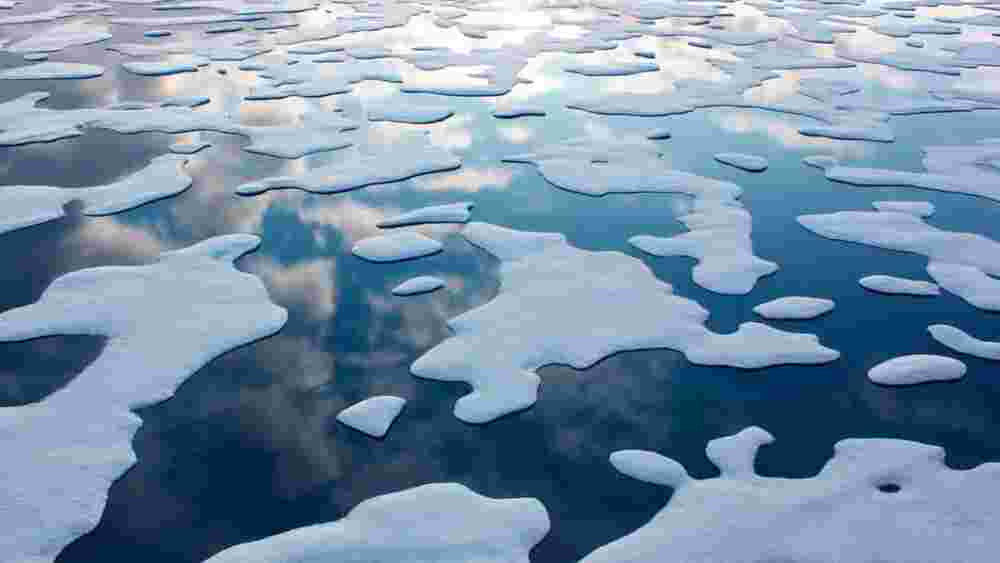
An innovative way is being created by scientists which will help them in “growing” ice and doing the impossible job of “refreezing” the Arctic Sea as initial tests prove promising.
Scientists are aiming at pumping seawater over the frozen Arctic Ocean. They have carried out trials in the Canadian Arctic which have seen sea ice getting thickened successfully.
According to a report published in New Scientist, if no action is taken right now, the accelerating climate change will make the Arctic “ice-free in the summer in the 2030s” which will be disastrous for the planet.