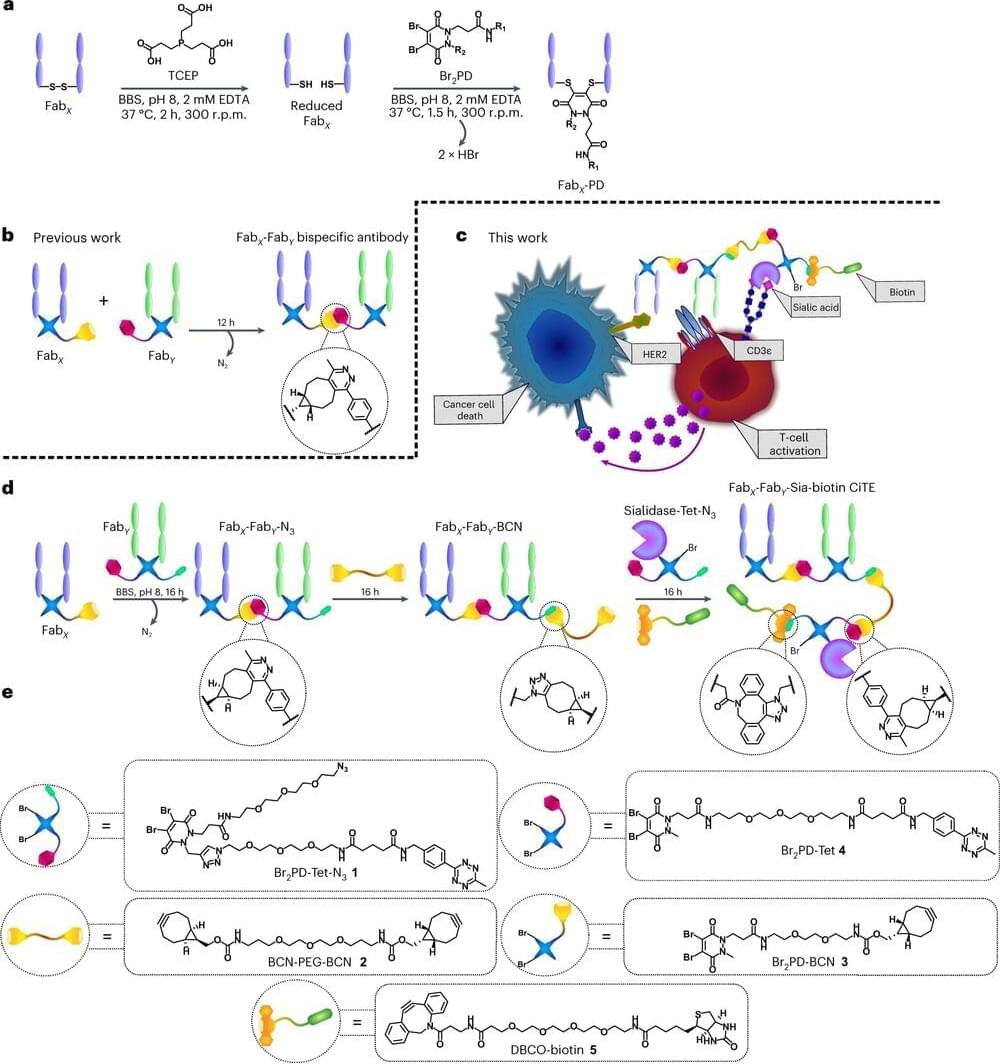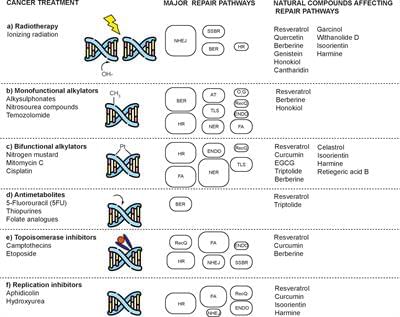
Resistance to current cancer treatments is an important problem that arises through various mechanisms, but one that stands out involves an overexpression of several factors associated with DNA repair. To counteract this type of resistance, different drugs have been developed to affect one or more DNA repair pathways, therefore, to test different compounds of natural origin that have been shown to induce cell death in cancer cells is paramount. Since natural compounds target components of the DNA repair pathways, they have been shown to promote cancer cells to be resensitized to current treatments. For this and other reasons, natural compounds have aroused great curiosity and several research projects are being developed around the world to establish combined treatments between them and radio or chemotherapy. In this work, we summarize the effects of different natural compounds on the DNA repair mechanisms of cancer cells and emphasize their possible application to re-sensitize these cells.
Day by day we are exposed to chemical carcinogens in the environment, ultraviolet (UV) radiation, ionizing radiation, and also those substances produced in our body during cellular metabolism that attack and produce a variety of DNA injuries. Each lesion favors the development of alterations in DNA and chromosomes, which favors oncogenic transformation and tumor progression. In order to reduce the number of changes in the genome and its instability, cells have several pathways of response to damage and DNA repair proteins that eliminate these lesions. DNA adducts, such as those created by alkylating agents, can be cleaved and repaired by base excision repair (BER) or by nucleotide excision repair (NER), depending on whether it is necessary to remove only a nitrogenous base or a nucleotide. Also, O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT), an alkyltransferase, eliminates alkylations.