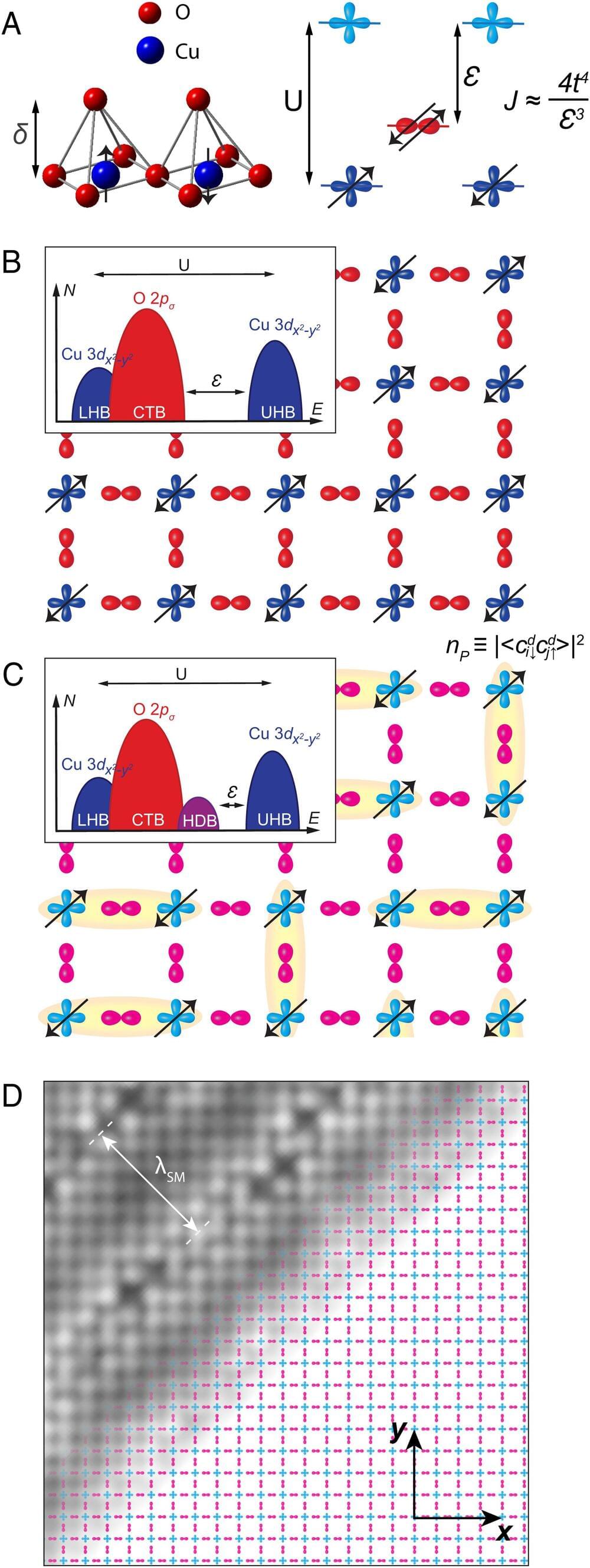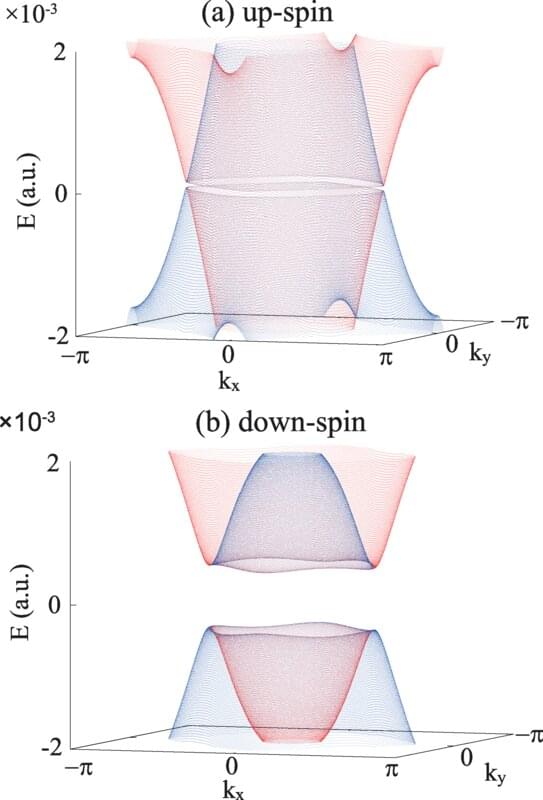
Topological materials that possess certain atomic-level symmetries, including topological insulators and topological semi-metals, have elicited fascination among many condensed matter scientists because of their complex electronic properties. Now, researchers in Japan have demonstrated that a normal semiconductor can be transformed into a topological semi-metal by light irradiation. Further, they showed how spin-dependent responses could appear when illuminated with circularly-polarized laser light. Published in Physical Review B, this work explores the possibility of creating topological semi-metals and manifesting new physical properties by light control, which may open up a rich physical frontier for topological properties.
Most ordinary substances are either electrical conductors, like metals, or insulators, like plastic. In contrast, topological insulators can exhibit unusual behavior in which electrical currents flow along the surface of the sample, but not inside the interior. This characteristic behavior is strongly connected to topological properties inherent in the electronic state. Furthermore, a novel phase called a topological semi-metal provides a new playground for exploring the role of topology in condensed matter. However, the underlying physics of these systems is still being pondered.
Researchers at the University of Tsukuba studied the dynamics of excitations in zinc arsenide (Zn3As2) when irradiated with a laser with circular polarization. Zinc arsenide is normally thought of as a narrow-gap semiconductor, which means that electrons are not free to move around on their own but can be easily propelled by energy from an external light source. Under the right conditions, the material can show a special topological state called a “Floquet-Weyl semi-metal,” which is a topological semi-metal coupled with light. In this case, the electrical current can be carried in the form of quasiparticles called Weyl fermions. Because these quasiparticles travel as if they have zero mass and resist becoming scattered, Weyl fermions can move easily through the material.